Nano Banana Inpaint: Complete 2025 Guide to Google AI Image Editing
Master Nano Banana inpaint for professional AI image editing. Complete 2025 guide covering the 4-step mechanism, prompting techniques, platform comparison, and troubleshooting tips.
Nano Banana Pro
4K-80%Google Gemini 3 Pro · AI Inpainting
谷歌原生模型 · AI智能修图
What is Nano Banana Inpaint?
Nano Banana inpaint represents a revolutionary approach to AI-powered image editing that emerged from Google DeepMind's research labs. The peculiar name originated during anonymous testing on LMArena, where the model appeared under the codename "nano-banana" before anyone knew it was Google's creation. The quirky designation combined "nano" for its compact model architecture and "banana" from an amusing bug where banana images randomly appeared in test results. When the model started trending for its exceptional editing capabilities, Google officially confirmed it as the Gemini 2.5 Flash Image model, though the community nickname has stuck ever since.
What makes Nano Banana inpaint fundamentally different from traditional image editing tools is its semantic understanding of visual content. Rather than working with pixels in isolation, the model comprehends the actual meaning and context of what it sees in your images. When you ask it to remove an unwanted object, it doesn't simply erase pixels and leave a blank space. Instead, it understands the surrounding environment, the lighting conditions, the textures present, and intelligently reconstructs what should naturally exist in that space. This contextual awareness extends to more complex tasks like changing someone's outfit, where the model must understand body positioning, fabric physics, and lighting interaction to produce believable results.
The inpainting capabilities specifically refer to the model's ability to selectively edit portions of an image while preserving everything else with pixel-perfect accuracy. Traditional inpainting in tools like Photoshop requires manual masking, careful feathering, and often multiple attempts to achieve seamless results. Nano Banana transforms this process into a conversational experience where you simply describe what you want changed, and the AI handles all the technical complexity behind the scenes. The model was officially released on August 26, 2025, with an enhanced Pro version following on November 20, 2025, bringing improved resolution support and more sophisticated reasoning capabilities.
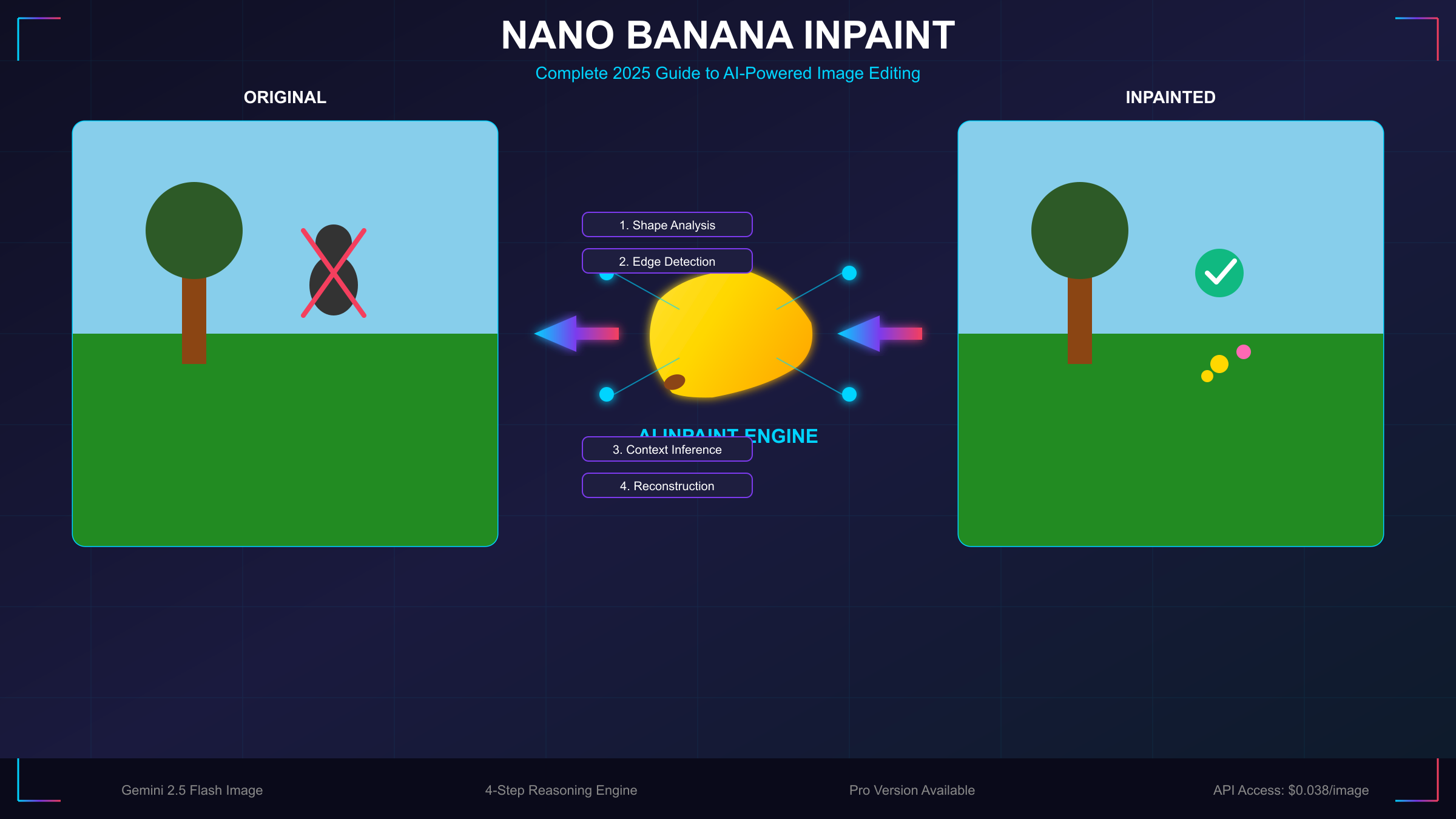
How the 4-Step Reasoning Mechanism Works
Understanding how Nano Banana processes inpainting requests reveals why it produces such remarkably natural results. Unlike simpler AI models that apply filters or transformations uniformly, Nano Banana employs a sophisticated four-step reasoning sequence that mirrors how a professional retoucher would approach an edit. This architectural decision, developed by the Google DeepMind team, enables the model to handle complex editing scenarios that would confuse less sophisticated systems.
The first step focuses on shape and geometry identification. When you mask a region or describe an area to edit, the model analyzes the three-dimensional structure implied by the two-dimensional image. It recognizes whether the masked area contains a flat surface like a wall, a curved object like a face, or a complex geometric form like furniture. This spatial understanding is crucial because it informs how replacement content should be rendered. A new object placed on a table must respect the table's perspective and angle, while a background replacement behind a person must understand the depth plane correctly.
The second step involves edge detection and boundary analysis. The model examines where the edited region meets the unedited portions of the image, calculating precise transition zones where blending must occur. This goes beyond simple alpha blending that you might achieve with layer masks in traditional software. The AI considers the characteristics of adjacent pixels, including their color gradients, texture patterns, and luminance values, to determine exactly how the new content should merge with existing elements. This edge intelligence prevents the telltale halos and hard boundaries that often reveal amateur photo manipulations.
In the third step, the model performs contextual interpretation of your prompt against the visual information. This is where the semantic understanding truly shines. When you request "remove the person and show what's behind them," the model must infer what reasonably exists in that occluded space based on visible context clues. It examines the room's style, the lighting direction, the flooring pattern, and uses this information to extrapolate convincing content. The model draws upon its training on millions of images to understand that a living room wall probably continues with similar paint color and texture, or that a beach extends with sand and water in predictable patterns.
The fourth and final step handles reconstruction with environmental matching. The AI generates new pixel data for the edited region while precisely matching the original image's lighting conditions, color palette, camera characteristics, and atmospheric qualities. This means a bright, sunny outdoor photo will have replacement content rendered with appropriate shadows and highlights, while a moody indoor scene will have edits that respect the ambient lighting. The model even considers subtle factors like film grain or digital noise patterns to ensure the edited region doesn't appear artificially clean compared to the rest of the photograph.
This four-step process happens in mere seconds, yet it accomplishes what might take a skilled Photoshop artist an hour or more of careful work. The results maintain what engineers call "photographic coherence," meaning the edited image appears as though it was captured in a single moment by a real camera, rather than assembled from disparate elements. Understanding this mechanism helps explain both the remarkable capabilities and the occasional limitations users encounter when pushing the technology to its edges.
Where to Access Nano Banana Inpaint
The Nano Banana inpaint technology is available through multiple platforms, each offering different interfaces, pricing structures, and feature sets. Choosing the right access point depends on your specific needs, whether you're a casual user wanting to edit personal photos, a content creator needing regular access, or a developer looking to integrate the technology into applications.
The most direct access comes through Google Gemini itself, where Nano Banana functions as the native image editing engine. Users with a Google account can access basic functionality for free, though the experience has evolved significantly since launch. Initially, free tier users enjoyed generous daily limits, but due to overwhelming demand, Google reduced free access to just 2-4 images per day in late 2025. Subscribers to Google AI Plus at $19.99 per month receive substantially higher quotas and priority access during peak usage periods. The Gemini interface offers the most seamless experience for users already embedded in Google's ecosystem, with natural language prompting and iterative editing capabilities built directly into the chat interface.
Higgsfield.ai provides a dedicated editing environment specifically optimized for Nano Banana Pro Inpaint. Their interface features a visual mask brush that lets you precisely define editing regions, along with quality level controls ranging from Low to High that balance generation speed against output fidelity. Higgsfield has become particularly popular among professional photographers and e-commerce sellers who need consistent, high-quality results. The platform offers straightforward credit-based pricing without subscription commitments, making it accessible for users with variable editing volumes.
The official nano-banana.com platform operates as a dedicated web application with comprehensive feature access. Their pricing structure starts with a free tier offering 20 credits for new users, with each standard image generation consuming 8 credits. Paid plans range from Lite at $4.90 monthly providing 6,000 yearly credits, through Pro at $14.50 monthly with 24,000 credits, up to Max at $45 monthly offering 60,000 credits. All paid tiers include commercial usage rights and watermark removal, making them suitable for business applications. The platform supports multiple input methods including direct upload, URL input, drag-and-drop, and clipboard pasting, providing flexibility in workflow integration.
| Platform | Free Tier | Paid Starting | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Gemini | 2-4 images/day | $19.99/month | Google ecosystem users |
| Higgsfield.ai | Limited trial | Credits-based | Professional photographers |
| nano-banana.com | 20 credits | $4.90/month | Regular content creators |
| WaveSpeed API | None | $0.038/image | Developers and automation |
For developers seeking programmatic access, WaveSpeed.ai offers a REST API implementation of the Nano Banana model. At $0.038 per image generation, approximately 26 images per dollar, this represents the most cost-effective option for high-volume applications. The API supports synchronous and asynchronous execution modes, multiple output formats including PNG, JPEG, and WebP, and the full range of aspect ratios from 1:1 through 21:9. The straightforward JSON request structure makes integration into existing applications relatively painless for developers familiar with REST APIs.
Step-by-Step Inpainting Tutorial
Learning to use Nano Banana inpaint effectively requires understanding both the technical workflow and the art of crafting effective prompts. This tutorial walks through the complete process from image upload to final export, using practical examples that demonstrate the technology's capabilities across different editing scenarios.
Preparing Your Image for Editing
Before starting any inpainting task, consider the source image quality carefully. Nano Banana performs best with high-resolution images where details are clearly visible, as the AI needs sufficient visual information to understand context and generate appropriate replacements. Images shot in good lighting with sharp focus yield significantly better results than dark, grainy, or blurry photographs. If your source image is low quality, consider running it through an upscaling tool first, as this provides the model with more data to work with during the editing process.
Upload your image through your chosen platform's interface. On Gemini, simply paste or attach the image to your chat. On Higgsfield or nano-banana.com, use the upload button or drag-and-drop functionality. The platforms accept common formats including JPEG, PNG, and WebP, with most supporting images up to 10 megabytes in size. Once uploaded, the image appears in your workspace ready for editing instructions.
Defining the Edit Region
The method for specifying what to edit varies by platform. On Higgsfield's Nano Banana Pro Inpaint interface, you use a brush tool to paint over the exact region you want modified. This masking approach offers precise control, allowing you to include or exclude specific elements with pixel-level accuracy. Brush size adjustments help you work efficiently on both large areas and fine details. When masking, it's often better to include slightly more area than necessary, as this gives the AI more context for blending while the protected regions remain completely untouched.
On Gemini and text-only interfaces, you define the edit region through your prompt description. Rather than painting a mask, you write something like "change the blue sofa to a brown leather chesterfield" or "remove the lamp from the table on the right side of the image." The AI's semantic understanding handles identifying the referenced objects, though complex scenes with multiple similar elements may require more specific descriptions. Including relative positions, colors, or other distinguishing features helps ensure the correct element is targeted.
Crafting Effective Edit Prompts
The quality of your prompt directly influences the quality of your results. Effective inpainting prompts share several characteristics that help the AI understand exactly what you want. Specificity matters enormously. Rather than writing "make it look better," describe precisely what changes you want: "remove the power lines from the sky and fill with matching cloudy sky texture" or "replace the man's casual t-shirt with a formal navy blue suit jacket."
Include relevant details about style, material, lighting, and context when applicable. If you're adding an object, describe its physical characteristics. If you're changing an existing element, specify both what to remove and what should appear instead. For complex edits, break them into sequential steps rather than attempting everything in a single prompt. Multi-turn editing, where you refine results through conversation, often produces better outcomes than trying to perfectly specify everything upfront.
Pro Tip: Save prompts that work well for your common editing tasks. Building a personal library of effective prompts accelerates future work and ensures consistent results across similar projects.
Three Common Inpainting Scenarios
Object removal represents one of the most frequent inpainting tasks. Whether eliminating photobombers from vacation shots, removing distracting background elements from product photography, or cleaning up unwanted signage from architectural images, the process follows a consistent pattern. Target the unwanted element specifically, then describe what should replace it. For background elements, prompts like "remove the trash can and continue the brick wall pattern naturally" guide the AI to generate contextually appropriate fills. The model excels when the surrounding area provides clear visual cues about what belongs in the edited space.
Outfit and appearance changes showcase Nano Banana's understanding of human subjects. You might prompt "change her casual sundress to an elegant evening gown in emerald green" for fashion experimentation, or "replace his glasses with stylish round tortoiseshell frames" for accessory testing. The AI maintains facial features, pose, and body positioning while transforming only the specified elements. This capability has significant applications in e-commerce, allowing brands to show products on models in various configurations without expensive reshoots.
Background replacement transforms the entire environment behind a subject while preserving the foreground with precise edge detection. Prompts like "replace the office background with a tropical beach at sunset" or "change the plain wall to an exposed brick loft setting" enable dramatic scene changes. The model handles complex hair edges, transparent elements, and subtle color spill with impressive accuracy, though very intricate edges may occasionally require multiple attempts or manual refinement.
Mastering Inpaint Prompts for Professional Results
The difference between amateur-looking edits and professional-quality results often comes down to prompt engineering. Through extensive testing and community feedback, certain prompting patterns have emerged as consistently effective for Nano Banana inpaint operations. Understanding these patterns accelerates your learning curve and helps you achieve reliable results across diverse editing scenarios.
The Anatomy of an Effective Inpaint Prompt
Successful inpainting prompts typically contain four key elements working together: the action verb, the target specification, the replacement description, and optional context modifiers. The action verb tells the model what operation to perform, whether removing, replacing, changing, adding, or transforming. The target specification identifies exactly which element in the image to affect. The replacement description defines what should appear instead. Context modifiers refine the result with details about style, lighting, texture, or other qualities.
Consider the difference between a basic prompt and an optimized version. A basic prompt might read: "Remove the person." An optimized prompt would specify: "Remove the man in the red jacket from the left side of the frame and fill the area with matching autumn forest background, maintaining the dappled sunlight pattern." The optimized version leaves no ambiguity about the target, provides explicit fill instructions, and ensures environmental consistency. While Nano Banana can work with minimal prompts, investing effort in detailed descriptions dramatically improves outcome quality.
Prompt Categories for Different Edit Types
Cleanup operations focus on removing unwanted elements while preserving the natural appearance of the image. Effective cleanup prompts explicitly describe how the vacated space should be filled. For sky cleanup, try "Remove all power lines and telephone poles, extending the gradient blue sky naturally." For surface cleanup, "Remove the coffee stain from the wooden table, matching the oak grain pattern and warm lighting." For crowd cleanup, "Remove the tourists in the background, showing the empty cobblestone plaza." These prompts work because they provide the model with clear direction about the expected result rather than leaving fill decisions entirely to the AI.
Restyle operations change the visual treatment of elements while preserving their core identity. Lighting changes work particularly well: "Transform the midday harsh lighting to golden hour warmth with long shadows falling to the left." Material changes can reimagine textures: "Change the fabric sofa to rich brown leather with visible grain and natural creasing." Seasonal transformations extend this concept: "Convert the summer garden scene to winter, adding frost on leaves and breath vapor from the person, while keeping their clothing and position identical." The key to restyle prompts is clearly defining what should change and what must remain constant.
Composition adjustments modify framing and perspective while maintaining photographic coherence. Outpainting extends the canvas: "Expand the frame leftward to show more of the garden path, continuing the gravel texture and hedge pattern." Reframing adjusts emphasis: "Simulate pulling back from a portrait to show more of the industrial warehouse environment behind the subject." Angle suggestions can shift perspective: "Generate what this product would look like from a 45-degree overhead angle, maintaining the same soft studio lighting." These prompts push the model's understanding of three-dimensional space and photographic principles.
Ten Essential Prompts for Common Scenarios
The following prompt templates address frequently encountered editing needs and can be adapted for your specific images:
Object Removal: "Remove [unwanted element] completely and fill with [contextually appropriate description matching surrounding area]."
Outfit Change: "Replace [subject's] current [clothing item] with [detailed description of new clothing including color, style, material, and fit]."
Background Swap: "Replace the entire background behind [subject] with [detailed environment description including lighting, atmosphere, and style]."
Weather Change: "Transform the scene to [weather condition] while preserving all foreground elements, adding appropriate [weather effects like rain, snow, fog]."
Time of Day: "Shift the lighting to [time period such as sunrise, midday, golden hour, dusk, or night] with natural [shadow directions and color temperature changes]."
These templates provide reliable starting points that you can customize with specific details for your images. The bracketed sections indicate where you should insert specifics relevant to your particular editing task.
Nano Banana vs Nano Banana Pro: Which Version Should You Choose?
Google released the original Nano Banana model, officially known as Gemini 2.5 Flash Image, on August 26, 2025. The Pro version, built on Gemini 3 Pro Image architecture, followed on November 20, 2025, bringing significant improvements across multiple dimensions. Understanding the differences between these versions helps you choose the right tool for your specific needs and budget.
The most immediately noticeable difference lies in resolution capabilities. The original Nano Banana maxes out at 1024 by 1024 pixels, which works adequately for social media content and web graphics but falls short for print-quality work or large-format displays. Nano Banana Pro dramatically expands this ceiling with support for 2K and 4K output, representing a fourfold increase in pixel count. For photographers delivering client work, e-commerce platforms needing zoomable product images, or any application requiring large-format reproduction, this resolution boost alone justifies the upgrade.
Text rendering accuracy represents perhaps the most transformative improvement in the Pro version. The original model frequently produced corrupted, illegible, or stylistically inconsistent text when asked to modify signs, labels, or any textual elements in images. This limitation severely constrained its usefulness for commercial applications where accurate branding matters. Pro versions render text correctly across multiple languages, various fonts, and diverse styling approaches. Signage modifications, product label changes, and UI mockup adjustments now produce reliable results, opening entirely new use cases for the technology.
| Feature | Nano Banana (Original) | Nano Banana Pro |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Resolution | 1024 x 1024 | Up to 4K |
| Generation Speed | ~3 seconds | 8-12 seconds |
| Text Rendering | Poor (frequent errors) | Excellent |
| Multi-Turn Reliability | ~40% consistency | ~60% consistency |
| Character Consistency | 95% accuracy | 96%+ accuracy |
| Complex Instructions | Limited understanding | Enhanced reasoning |
The Pro model also demonstrates substantially improved reasoning capabilities when handling complex, multi-part instructions. Where the original might struggle with prompts containing multiple conditions or spatial relationships, Pro's enhanced logic handles these scenarios more reliably. Instructions like "remove the person on the left but keep the person on the right, and change only the left person's background to a beach while maintaining the original background for the right person" would likely confuse the original model but fall within Pro's processing capabilities.
Generation speed represents a tradeoff rather than an improvement. The original Nano Banana produces results in approximately 3 seconds, making it excellent for rapid iteration and experimentation. Pro takes 8-12 seconds per generation, reflecting the additional computation required for higher resolution and more sophisticated processing. For workflows prioritizing speed over maximum quality, the original version may actually be preferable. Many users adopt a hybrid approach, using the faster original model for exploration and initial concepts, then switching to Pro for final production-quality outputs.
Multi-turn editing reliability, where you refine an image through successive conversation turns, improves approximately 60% with the Pro version. The original model sometimes introduced unwanted changes during iterative refinement, unexpectedly altering elements you intended to preserve. Pro's enhanced memory and consistency tracking significantly reduces this drift, making it practical to develop images through extended editing sessions without accumulating errors.
Pricing considerations also factor into version selection. Both models are accessible through Google AI Plus subscriptions at $19.99 monthly, but the Pro model consumes substantially more computational resources, which translates to tighter rate limits and higher per-image costs through third-party APIs. For high-volume applications, the original model's lower resource requirements may offer better value, especially when Pro-level quality isn't essential for every image.
Troubleshooting Common Nano Banana Issues
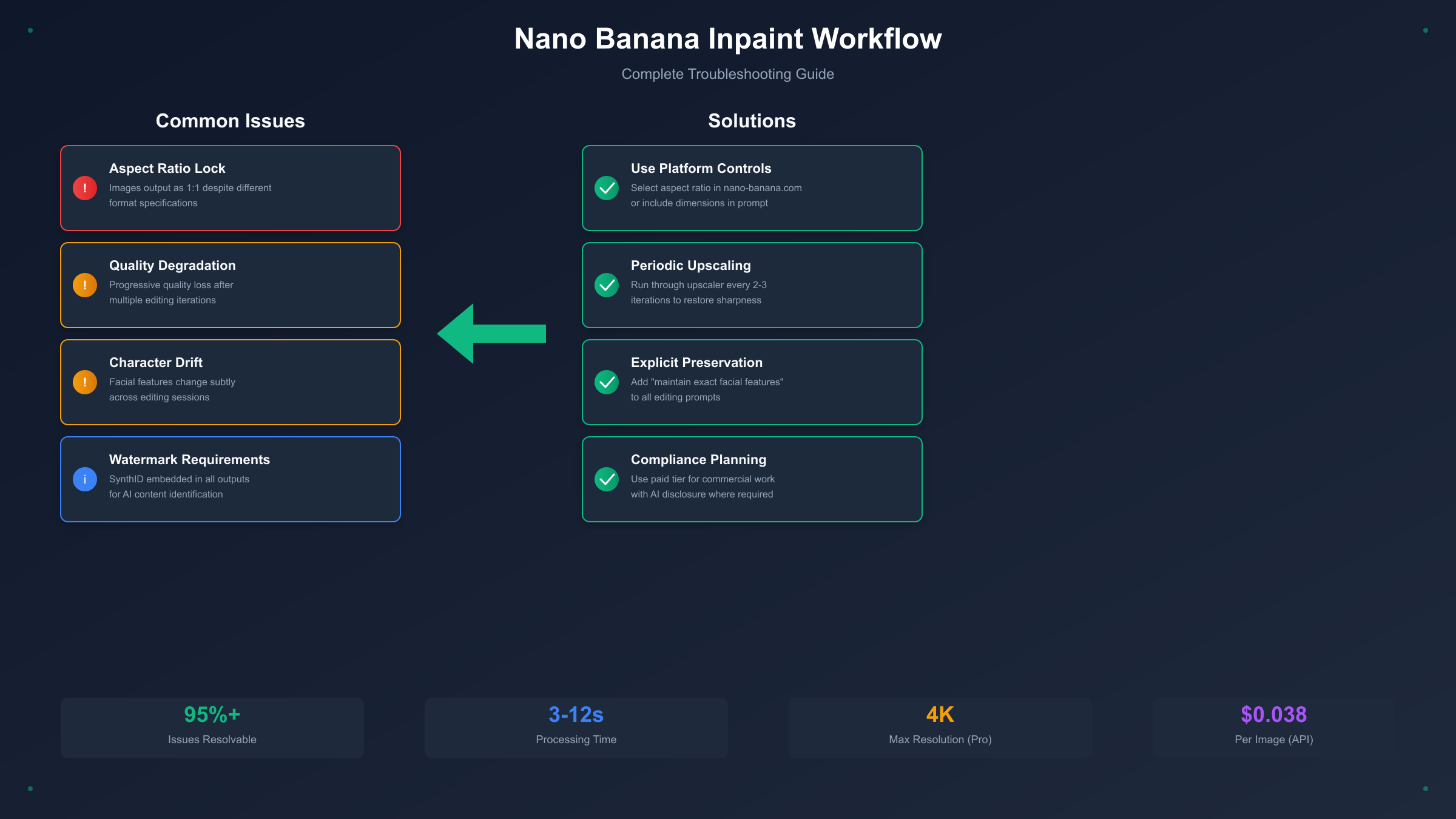
Despite its impressive capabilities, Nano Banana users regularly encounter specific technical challenges that can frustrate newcomers. Understanding these common issues and their solutions transforms your experience from trial-and-error frustration into confident problem-solving. The challenges fall into several categories, each with proven workarounds developed by the user community.
Aspect Ratio Lock Problems
One of the most frequently reported issues involves the model stubbornly producing square 1:1 images regardless of specified dimensions. Users requesting 16:9 landscape images for YouTube thumbnails or 9:16 portrait formats for social media stories find their requests ignored, receiving square outputs instead. This behavior appears connected to server load and quota management, though Google hasn't officially confirmed the underlying cause.
The most effective workaround involves using platform interfaces that explicitly support aspect ratio selection, such as nano-banana.com or third-party API implementations. When working within Gemini directly, try including aspect ratio descriptions within your prompt itself: "Create a wide landscape composition with 16:9 proportions showing..." rather than relying solely on format settings. Some users report success by generating at 1:1 and then using outpainting to extend the canvas to desired proportions, though this adds an extra step to the workflow.
Quality Degradation After Multiple Edits
Iterative refinement, where you make several sequential edits to develop an image toward your vision, often introduces progressive quality loss. After three or four editing rounds, images may exhibit noticeable pixelation, softening of details, or subtle color shifts compared to the original. This degradation accumulates because each generation introduces compression artifacts and minor imperfections that compound through successive operations.
Professional workflows address this limitation by planning edit sequences carefully to minimize iteration count. Rather than making many small adjustments, craft more comprehensive prompts that accomplish multiple changes simultaneously. When extensive iteration is unavoidable, periodically run the image through an upscaling tool to restore sharpness before continuing edits. Some platforms offer built-in upscaling integration specifically to combat this issue. Additionally, saving intermediate versions at each major milestone allows you to backtrack if a particular edit path introduces unacceptable degradation.
Consistency Drift in Character Features
While Nano Banana generally maintains excellent identity preservation when editing portraits, subtle drift can occur during extended editing sessions. A person's facial expression might shift slightly, eye color may vary across iterations, or distinctive features like birthmarks might appear or disappear. This drift becomes particularly problematic for commercial projects requiring precise character consistency across multiple images.
Mitigation strategies include using explicit preservation language in prompts: "Maintain exact facial features, eye color, and all identifying characteristics while changing only the background." Providing reference images when possible helps anchor the model's understanding of what should remain constant. For critical projects, some professionals use external face-locking tools that extract and restore facial regions after Nano Banana completes other edits, ensuring absolute identity fidelity at the cost of additional workflow complexity.
Watermark and Policy Compliance
Every Nano Banana output includes both a visible watermark (on free tier) and Google's invisible SynthID mark identifying AI-generated content. While the visible watermark can be removed on paid tiers, the SynthID remains embedded in the image data as part of Google's commitment to AI transparency. This watermarking raises considerations for commercial and editorial use where AI-generated content disclosure may be required or preferred.
Understanding your jurisdiction's regulations regarding AI-generated content helps navigate compliance requirements. Many professional contexts now explicitly require disclosure of AI involvement in image creation, making the SynthID actually advantageous for maintaining ethical standards. For applications where any watermarking is unacceptable, alternative AI editing tools without such requirements exist, though they may lack Nano Banana's specific capabilities and quality levels.
Advanced Tips and API Integration for Developers
Moving beyond casual use into professional production workflows requires understanding the deeper capabilities and integration options available with Nano Banana. Developers and power users can leverage API access to build custom applications, automate editing pipelines, and integrate AI-powered inpainting into existing software systems.
API Architecture and Implementation
The WaveSpeed.ai API provides RESTful access to Nano Banana's capabilities through a straightforward request-response pattern. Each image edit requires a POST request containing the source image (as URL or base64), your text prompt, and optional parameters for aspect ratio, output format, and quality settings. The API returns a prediction ID for asynchronous processing, with results available through a GET request once generation completes. For latency-sensitive applications, synchronous mode returns results directly in the initial response, though this approach ties up connections during processing.
Pricing at $0.038 per image generation makes API access economically viable for production workloads. A budget of $100 provides approximately 2,600 image edits, which translates to substantial capacity for most commercial applications. The cost structure favors batch processing and automated pipelines over manual one-off edits, as the per-image cost remains constant regardless of volume. This predictable pricing enables accurate budgeting for projects with defined image processing requirements.
Building Automated Editing Pipelines
Production workflows benefit significantly from automation that leverages Nano Banana's natural language interface. Consider an e-commerce scenario where product photographers capture items in a standard studio setup, then need variations showing products in different lifestyle contexts. An automated pipeline might accept the studio photograph, apply a series of background replacement prompts generating beach, office, and home environment variations, then output all versions to a content management system for catalog use.
Such pipelines typically implement retry logic for handling occasional generation failures, quality validation to catch problematic outputs before they reach production, and parallel processing to maximize throughput within rate limits. The API's support for multiple output formats and configurable aspect ratios enables single-request generation of assets optimized for different platforms, from square Instagram posts to wide banner advertisements.
Developer Tip: When building production pipelines, implement exponential backoff for retries and maintain a local cache of successful prompts. This reduces costs by avoiding repeated experimentation and improves reliability during high-load periods.
Integration Patterns for Existing Applications
Incorporating Nano Banana capabilities into existing software follows several common patterns depending on application architecture. For web applications, serverless functions provide a natural integration point, accepting image URLs and prompts from client applications and returning edited results. This pattern isolates API credentials from client code while enabling scalable processing. Desktop applications might integrate directly, bundling API calls within editing workflows and providing real-time feedback as edits generate.
Mobile applications face additional considerations around image upload sizes and network latency. Compressing images before API submission reduces upload times without significantly impacting edit quality, as the model works effectively with reasonably compressed sources. Displaying generation progress through spinners or estimated wait times maintains user engagement during the 3-12 second processing window typical of Nano Banana requests.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Professional users seeking to minimize API costs while maintaining quality employ several optimization strategies. Batching related edits into single sessions reduces overhead compared to scattered individual requests. Using the faster, cheaper original model for initial concept exploration before switching to Pro for final outputs halves costs on exploratory work. Implementing local caching prevents repeated API calls for identical edit requests, which commonly occurs in development and testing environments.
For teams requiring reliable, high-volume API access, services like laozhang.ai provide optimized routing to AI model endpoints with additional benefits including transparent billing, technical support, and stable connectivity. Such intermediary services prove particularly valuable for users in regions with connectivity challenges to direct Google infrastructure, offering improved reliability without sacrificing quality or increasing per-request costs significantly.
Quality Assurance in Automated Workflows
Automated pipelines must implement quality gates that catch problematic outputs before they propagate downstream. Common validation checks include resolution verification ensuring outputs meet minimum pixel dimensions, face detection confirming portraits retain expected subjects, and perceptual hashing to identify generations that drift excessively from source images. More sophisticated systems employ secondary AI models to evaluate edit quality, flagging outputs that exhibit artifacts, unrealistic lighting, or semantic inconsistencies for human review.
Logging and monitoring become critical at scale, enabling teams to identify prompt patterns that consistently produce poor results, track success rates across different edit types, and optimize prompts based on historical performance data. This data-driven approach to prompt engineering continuously improves output quality while reducing wasted generation credits on unsuccessful attempts.
Comparing Nano Banana to Traditional Editing Tools
Understanding where Nano Banana excels and where traditional tools remain necessary helps professionals build optimal workflows that leverage the strengths of each approach. The choice isn't binary; the most effective modern editing workflows combine AI capabilities with traditional software in complementary ways.
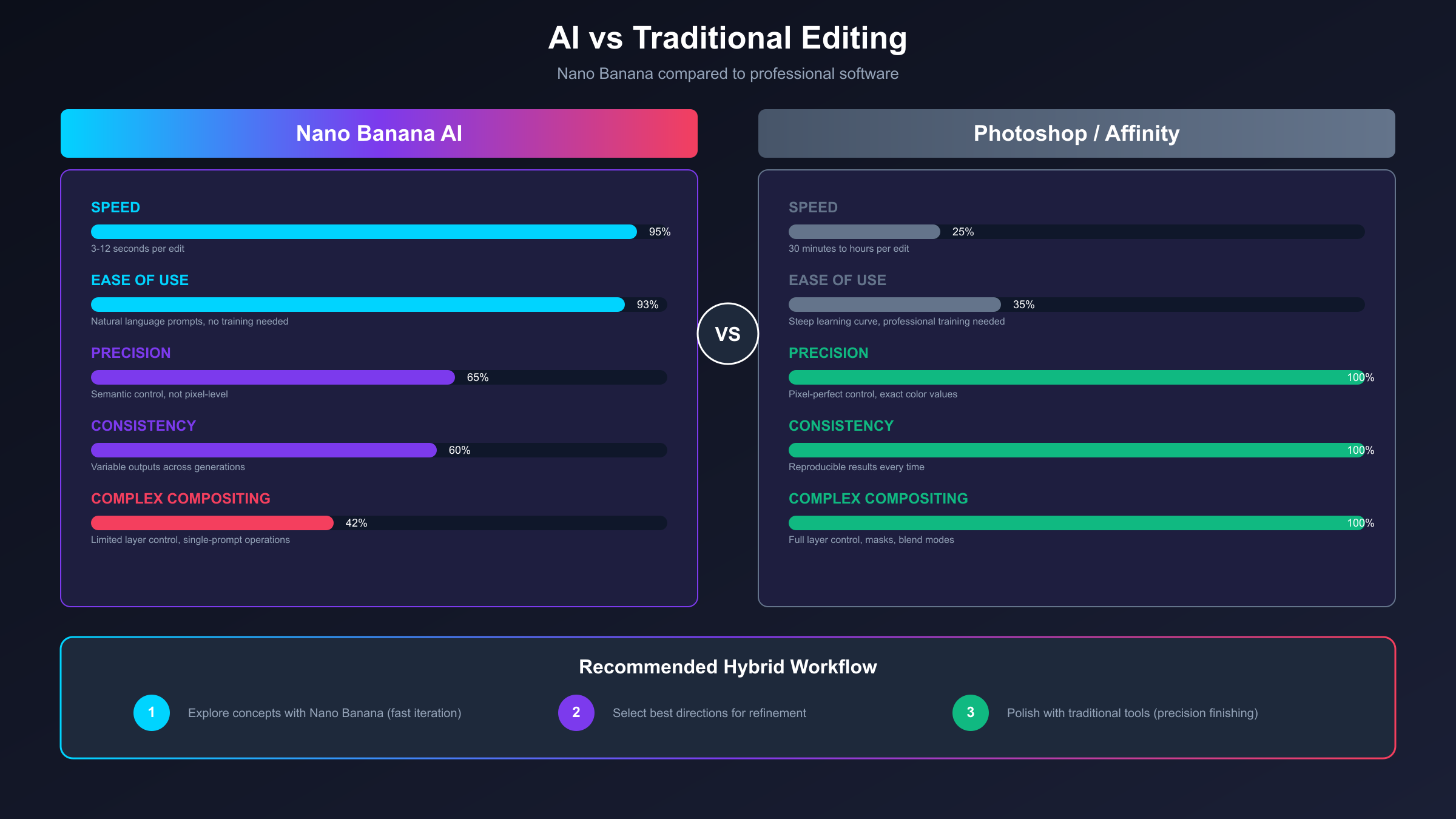
Speed represents Nano Banana's most dramatic advantage over traditional editing software. Tasks that would require 30 minutes to an hour in Photoshop, such as removing a complex background, changing someone's outfit, or replacing multiple objects in a scene, complete in seconds with appropriate prompting. For content creators producing high volumes of images under tight deadlines, this acceleration transforms previously impractical workflows into routine operations. A social media manager who once spent entire afternoons preparing visual content can now accomplish the same output in minutes.
However, traditional tools maintain clear advantages in precision and control. When exact pixel-level adjustments matter, when brand guidelines demand specific color values, or when complex compositing requires multiple layers with independent control, professional software like Adobe Photoshop or Affinity Photo remains essential. Nano Banana operates as a black box; you describe desired outcomes rather than controlling individual parameters. For applications requiring absolute precision, this limitation proves significant.
The hybrid workflow many professionals adopt leverages both approaches strategically. Nano Banana handles initial creative exploration, generating multiple concept variations rapidly until finding promising directions. Traditional tools then refine selected concepts with precision adjustments, color correction, and final touches that require exact control. This combination maximizes creative throughput while maintaining professional quality standards.
| Aspect | Nano Banana | Traditional Software |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Seconds per edit | Minutes to hours |
| Precision | Natural language control | Pixel-level control |
| Learning Curve | Minimal | Extensive |
| Consistency | Variable outputs | Reproducible results |
| Complex Compositing | Limited | Full capability |
| Cost (per edit) | $0.038-0.10 | Software subscription only |
Creative experimentation benefits particularly from Nano Banana's rapid iteration capabilities. Designers can explore dozens of variations in the time traditional workflows would allow for just a few, discovering unexpected directions that might never emerge from slower processes. This expanded creative range often leads to better final outcomes, as more possibilities receive evaluation before commitment to production effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is Nano Banana, and why the unusual name?
Nano Banana is Google's AI-powered image editing model that emerged from their Gemini project. The quirky name originated during anonymous testing on LMArena, where the model appeared as "nano-banana" before Google publicly claimed it. The nickname combines "nano" for the compact model architecture and "banana" from a bug that occasionally inserted banana images into test outputs. Despite the playful origin, the technology represents serious advancement in semantic image editing, officially built on Gemini 2.5 Flash Image architecture with a Pro version released in November 2025.
How does Nano Banana inpainting differ from Photoshop's content-aware fill?
While both tools aim to intelligently fill regions of images, they work fundamentally differently. Photoshop's content-aware fill analyzes surrounding pixels and attempts to replicate patterns statistically. Nano Banana employs deep semantic understanding, comprehending what objects mean rather than just their pixel patterns. This enables Nano Banana to generate contextually appropriate content that respects lighting, perspective, and logical relationships, while also allowing natural language specification of what should appear in edited regions rather than simply extending existing patterns.
Is Nano Banana free to use, and what are the limitations?
Google offers limited free access through Gemini, typically allowing 2-4 images per day depending on current demand. This free tier provides adequate access for casual experimentation but proves insufficient for production work. Paid access through Google AI Plus at $19.99 monthly significantly expands quotas. Third-party platforms and APIs offer alternative pricing models, with API access through services like WaveSpeed costing approximately $0.038 per image, providing more flexible options for varying usage patterns.
Can I use Nano Banana outputs commercially?
Commercial use is permitted on paid tiers that remove visible watermarks. However, all outputs contain Google's invisible SynthID watermark identifying AI-generated content, which cannot be removed. Depending on your jurisdiction and industry, disclosure of AI involvement in image creation may be required or advisable. Review relevant regulations and platform policies before incorporating AI-edited images into commercial materials, particularly for advertising, editorial, or product photography applications.
What image formats and sizes work best with Nano Banana?
The model accepts common formats including JPEG, PNG, and WebP, with file sizes typically capped at 10 megabytes depending on platform. Higher resolution source images generally produce better results, as they provide the AI more visual context for editing decisions. The original Nano Banana outputs at maximum 1024x1024 pixels, while the Pro version supports up to 4K resolution. For best results, provide source images at or above your desired output resolution.
Your Next Steps with Nano Banana Inpaint
The introduction of Nano Banana inpaint marks a genuine inflection point in image editing accessibility. Tasks previously requiring years of Photoshop expertise now yield to natural language descriptions that anyone can write. This democratization doesn't eliminate the value of traditional skills but rather redirects creative energy from technical execution toward conceptual exploration and artistic direction.
For newcomers, the lowest-friction entry point remains Google Gemini's free tier. Experiment with simple edits on personal photographs to develop intuition for effective prompting before investing in paid access or specialized platforms. Pay attention to which prompt patterns produce reliable results and which lead to frustration, building your personal knowledge base of effective techniques.
Professionals evaluating Nano Banana for production workflows should begin with controlled experiments on non-critical projects, establishing realistic expectations for quality, speed, and consistency before depending on the technology for deadline-driven work. The hybrid approach combining AI-powered rapid iteration with traditional finishing provides an effective bridge as you determine the optimal balance for your specific applications.
The technology continues evolving rapidly, with Google regularly releasing improvements to both the core model and available features. Staying current with developments ensures you leverage the latest capabilities while avoiding deprecated approaches. The community of Nano Banana users actively shares discoveries and techniques, making engagement with forums and social media channels valuable for continuous learning.
Whether you're a photographer seeking to accelerate client delivery, a marketer needing visual content at scale, or a developer building the next generation of creative applications, Nano Banana inpaint provides capabilities that would have seemed impossible just a year ago. The future of image editing has arrived, and it speaks your language.