- Home
- /
- Blog
- /
- API Troubleshooting
- /
- Gemini Tier 1 Billing Enabled but Still Getting Free Quotas (250 RPD)? Complete Fix Guide 2026
Gemini Tier 1 Billing Enabled but Still Getting Free Quotas (250 RPD)? Complete Fix Guide 2026
Fix the Gemini API tier mismatch where billing shows Tier 1 but quotas stay at free level (250 RPD). Covers 5 root causes, step-by-step solutions, and tier verification methods.
Developers enabling billing on their Google Cloud project expect Gemini API rate limits to jump from free tier levels to Tier 1 capacity, but many discover their quotas remain stuck at 250 RPD or similar free tier values. This is a known issue with multiple root causes, and the most common fix involves switching from experimental model variants like gemini-2.5-pro-exp to stable or preview-paid variants, then regenerating your API key in Google AI Studio. This guide systematically walks through every root cause and provides verified solutions based on Google AI Developer Forum reports and official documentation current as of February 2026.

TL;DR
If your Gemini API is showing free tier limits despite having billing enabled, here is the quick checklist before diving into the full guide. The most frequent cause is using an experimental model variant that remains on free tier limits regardless of your billing status. Switch to a stable model like gemini-2.5-pro or a paid preview variant, regenerate your API key from within the billing-enabled project in AI Studio, and allow up to 48 hours for billing synchronization. If those steps do not resolve it, verify that promotional free credits are not overriding your paid tier, and consider contacting Google Cloud support as a last resort. The sections below provide detailed explanations for each scenario and verified solutions drawn from developer community reports.
Why Your Tier 1 Billing Shows Free Tier Quotas
The disconnect between your billing dashboard showing "Tier 1" and your API returning free tier rate limits is one of the most frustrating developer experiences in the Gemini ecosystem. Multiple threads on the Google AI Developers Forum document this exact scenario: developers carefully follow the official steps to enable billing, see confirmation that their project is on Tier 1, yet continue hitting 429 "Resource Exhausted" errors at rates well below what paid tier limits should allow. Understanding why this happens requires examining how Google's billing and quota systems actually interact, because they are not as tightly coupled as most developers assume.
The fundamental issue is that Google's Gemini API uses a multi-layered system where billing status, project tier assignment, and actual per-model rate limits operate somewhat independently. When you enable billing on your Google Cloud project, the system correctly registers your project as eligible for Tier 1. However, the actual rate limits applied to your API requests depend on several additional factors: which specific model variant you are calling, whether your API key was generated in the correct project, and whether the billing-to-quota synchronization has completed. This layered architecture means that any single point of failure in the chain can result in the symptoms you are experiencing, even when your billing dashboard looks completely correct.
What makes this particularly confusing is that Google's official rate limits documentation page, last updated on February 19, 2026, no longer publishes specific RPM and RPD numbers for each tier. Instead, it directs developers to check their actual limits in Google AI Studio. This change removed the easy reference point that developers previously used to verify their tier status, creating an additional layer of uncertainty. If you are looking for a detailed guide to Gemini API free tier capabilities, our comprehensive resource covers everything you need to know about what is included at the free level and how it compares to paid tiers.
The good news is that this problem is well-documented, and the root causes are identifiable. The sections below systematically walk through each cause and its corresponding fix, ordered by how frequently each cause appears in developer community reports. Most developers resolve the issue within the first two steps.
Understanding Gemini API Tiers and Rate Limits (2026)

Google structures Gemini API access into four distinct tiers, each with its own requirements and rate limit allocations. Understanding exactly what each tier provides is essential for diagnosing why your quotas might not match your expectations. The tier system determines your maximum requests per minute (RPM), requests per day (RPD), and tokens per minute (TPM) across different model families.
The Free Tier requires only that you are in an eligible country, and it provides basic access with notably restricted limits. Based on data from SERP sources cross-referenced with AI Studio observations, free tier limits for Gemini 2.5 Pro sit around 5 RPM and 100 RPD, while Gemini 2.5 Flash offers approximately 10 RPM and 250 RPD. The 250 RPD figure is the one most developers encounter when they are stuck on free tier without realizing it. Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite provides slightly more generous free limits at roughly 15 RPM and 1,000 RPD. It is worth noting that Google significantly reduced free tier quotas in December 2025, cutting them by approximately 50-80% from their previous levels, which made this issue much more noticeable for developers who were previously operating comfortably within free tier limits.
Tier 1 unlocks when you link a full paid billing account to your Google Cloud project. This tier dramatically increases rate limits, with sources indicating approximately 150-300 RPM and 1,500 or more RPD for models like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Flash. The jump from free to Tier 1 represents a 6-15x increase in daily request capacity, which is why developers notice the mismatch so acutely. A critical nuance that the official documentation emphasizes is that "rate limits are more restricted for experimental and preview models" even on paid tiers, meaning not all models benefit equally from a Tier 1 upgrade.
Tier 2 requires a cumulative spend of at least $250 plus 30 days since your first payment, while Tier 3 raises the threshold to $1,000 cumulative spend plus 30 days. These higher tiers progressively increase rate limits and unlock additional capabilities. For a complete breakdown of Gemini API rate limits across all tiers, our dedicated guide covers the full spectrum of limits including TPM, context caching, and batch processing quotas.
The pricing structure for paid tiers is also worth understanding in the context of this issue. Based on the official Google pricing page verified on February 21, 2026, Gemini 2.5 Pro charges $1.25-$2.50 per million input tokens and $10.00-$15.00 per million output tokens, with the range depending on context length. Gemini 2.5 Flash is significantly more affordable at $0.30-$1.00 per million input tokens and $2.50 per million output tokens, making it the preferred choice for high-volume applications. The newer Gemini 3.1 Pro Preview commands premium pricing at $2.00-$4.00 per million input tokens and $12.00-$18.00 per million output tokens, but this model is currently only available in preview with more restricted rate limits. Understanding these pricing tiers helps you estimate costs once your Tier 1 billing is properly activated, and ensures you are not surprised by charges when the free tier restrictions are finally lifted.
One important detail that catches many developers off guard: rate limits apply per project, not per API key. This means creating multiple API keys within the same project does not multiply your quotas. It also means that if you have API keys in different projects with different billing configurations, the rate limits you experience will vary depending on which key you use, which directly connects to one of the root causes explored in the next section. Additionally, RPD quotas reset at midnight Pacific Time, and the rate limit values you see may differ between what is displayed in the Cloud Console quotas page and what the API actually enforces, due to the distinction between configured quotas and dynamically applied tier limits.
The 5 Root Causes Behind This Issue
The billing-quota mismatch has five distinct root causes, each requiring a different fix. Based on analysis of dozens of Google AI Developers Forum threads and community reports, these are ordered by frequency of occurrence. Understanding which root cause applies to your situation is the fastest path to resolution.
Root Cause 1: Model Variant Confusion (Most Common, ~60% of Cases)
This is the single most overlooked cause of the tier mismatch, and it is the one that most troubleshooting guides fail to explain clearly. Google maintains multiple variants of each model, and the naming convention directly determines whether your requests use paid tier limits or remain on free tier limits regardless of your billing status. Model names ending in -exp or -experimental are explicitly designated as free tier models. For example, gemini-2.5-pro-exp-03-25 will always operate under free tier quotas no matter what billing configuration you have set up. By contrast, the stable variant gemini-2.5-pro and the paid preview variant gemini-2.5-pro-preview-03-25 will respect your Tier 1 billing and apply the higher rate limits accordingly. This distinction is buried in the official documentation and rarely called out in the error messages developers receive, making it an easy trap to fall into, especially when following tutorials or sample code that happens to use an experimental variant.
Root Cause 2: API Key Not Linked to Billing Project (~20% of Cases)
Google AI Studio allows you to create API keys associated with different Google Cloud projects. If you created your API key in a project that does not have billing enabled, or if you have multiple projects and accidentally selected the wrong one, your API calls will use the free tier limits of the non-billing project. This is particularly common when developers have both a personal project and a work project, or when they created their initial API key during a free trial and never regenerated it after enabling billing. The fix is straightforward: go to AI Studio, check which project your API key belongs to, and if necessary, create a new key specifically within the project that has billing configured. For developers who are also experiencing troubleshooting invalid API key issues, the key-project linkage is often the underlying cause.
Root Cause 3: Billing Synchronization Delay (~10% of Cases)
When you first enable billing or change your billing configuration, there is a synchronization period before the new tier limits take effect across all Google systems. Forum reports consistently indicate this delay can range from a few minutes to up to 48 hours, with most synchronizations completing within 24 hours. During this window, your billing dashboard will correctly show Tier 1, but the rate limiting system may still enforce free tier quotas. Making a small paid API call using a non-free model can sometimes help trigger the synchronization process more quickly, as it forces the billing system to register an actual chargeable event.
Root Cause 4: Free Promotional Credits Override (~5% of Cases)
If your Google Cloud account has active promotional credits, such as the $300 free trial credit or other promotional offers, the system may treat your account as a free tier user despite having a payment method on file. This is because promotional credits are technically not the same as a paid billing account from the tier system's perspective. Developers who signed up for Google Cloud's free trial and then added a payment method sometimes find that their account remains on free tier limits until the promotional credits are fully consumed or expired. The distinction matters because the tier upgrade requires a "full paid billing account," which Google interprets as an account actively generating charges against a real payment method, not one drawing down promotional balance.
Root Cause 5: Preview Model Restrictions (~5% of Cases)
Even on paid tiers, preview models operate under more restricted rate limits than their stable counterparts. The official documentation explicitly states that "rate limits are more restricted for experimental and preview models," but it does not provide specific numbers for preview model limits, directing developers to check AI Studio instead. If you are using a model like Gemini 3.1 Pro Preview or Gemini 3 Pro Preview, the rate limits you experience may be significantly lower than what you would get with stable models on the same tier. This is not technically a bug but rather an intentional design decision by Google to manage capacity for models that are still being refined and evaluated. It particularly affects developers who are fixing 429 errors in Gemini image generation where preview models are often the only option for new capabilities like native image generation.
There is also a particularly frustrating variant of this problem that some developers call the "dead loop" scenario. In this case, billing is properly enabled, the project shows Tier 1 status, the correct model variant is being used, and the API key is in the right project, yet the billing dashboard shows exactly zero usage and zero charges. The rate limiting system cannot detect any billable API activity, which prevents the tier from fully activating. This circular dependency, where you need to make paid API calls to trigger the tier but the tier restrictions prevent the calls from being treated as paid, has been reported in multiple forum threads without a definitive official solution. The most successful workaround reported by developers is to explicitly make calls to a stable, non-experimental model with a small prompt, wait 24-48 hours, and then check whether the billing dashboard begins registering charges. If it does not, this particular scenario requires escalation to Google Cloud support for manual tier activation.
Step-by-Step Fix Guide
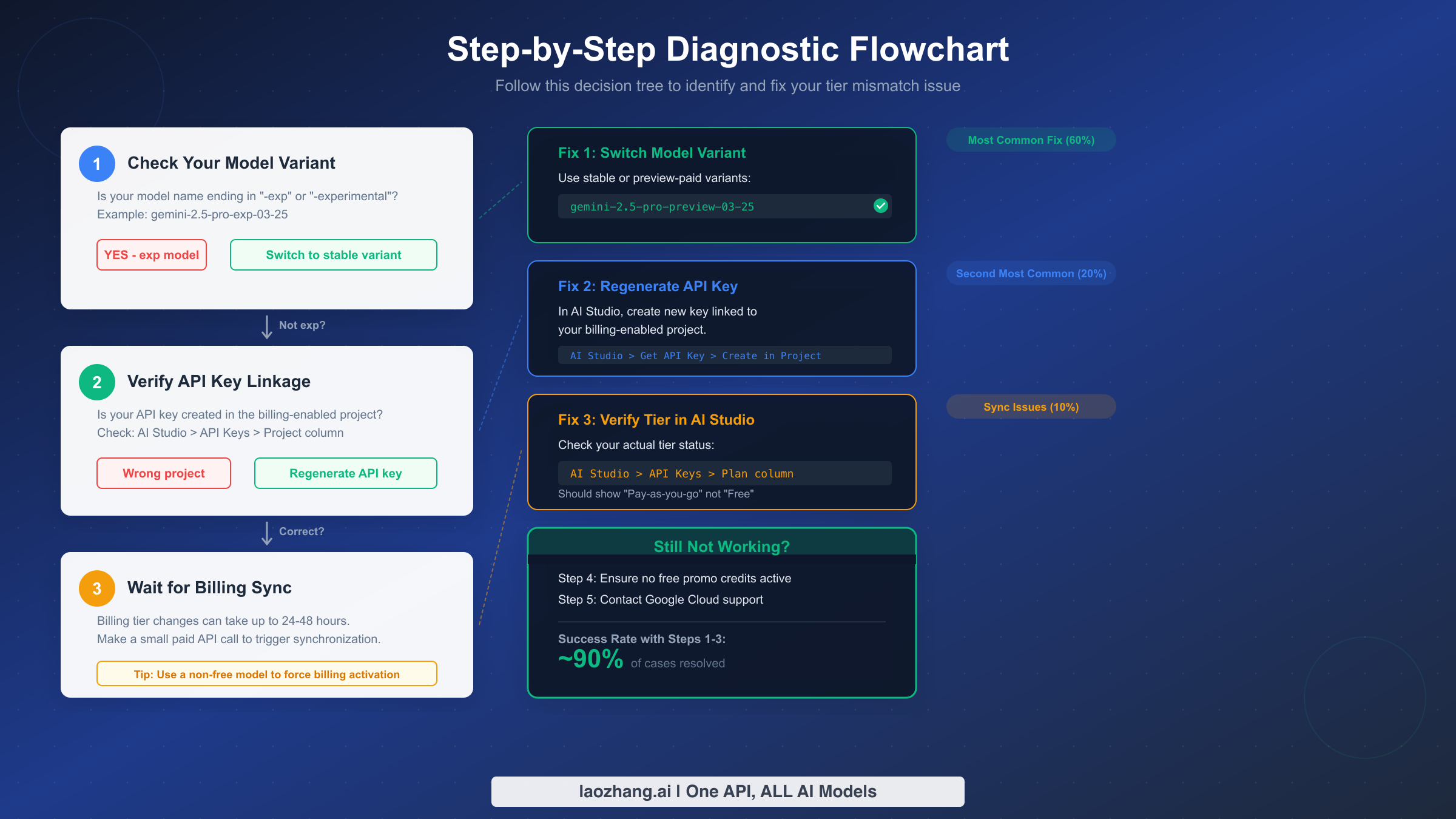
Now that you understand the root causes, here is the systematic approach to fix your tier mismatch. Follow these steps in order, as they are arranged from most likely to resolve the issue to least likely, ensuring you fix the problem as quickly as possible.
Fix 1: Verify and Switch Your Model Variant
Start by checking exactly which model identifier you are sending in your API requests. Open your application code or API call configuration and look at the model parameter. If it contains -exp, -experimental, or refers to a model that is only available as a free variant, this is almost certainly your problem. The fix is to switch to the equivalent stable or paid preview variant. Here is a quick reference for the most commonly confused model names:
gemini-2.5-pro-exp-03-25(FREE) → Switch togemini-2.5-pro(PAID Tier 1+)gemini-2.5-flash-exp(FREE) → Switch togemini-2.5-flash(PAID Tier 1+)- Any model with
-expsuffix → Find the equivalent without-exp
You can verify available model variants and their tier eligibility directly in Google AI Studio under the model selector. Models that support paid tier limits will be marked accordingly in the interface. After switching the model variant, make a test API call and check whether the rate limit headers in the response reflect your Tier 1 allocation. Here is a quick verification you can run with curl to check your effective limits:
hljs bashcurl -s -D - "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-2.5-pro:generateContent?key=YOUR_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"contents":[{"parts":[{"text":"Hello"}]}]}' 2>&1 | grep -i "x-ratelimit"
The response headers will show your actual rate limit allocation. If you see values like x-ratelimit-limit-requests-per-day: 250, you are still on free tier. Tier 1 values should show significantly higher numbers like 1500 or more for RPD. This quick test definitively confirms whether your model variant and API key configuration are correctly using paid tier limits.
Fix 2: Regenerate Your API Key in the Correct Project
If switching the model variant did not resolve the issue, the next step is to verify and potentially regenerate your API key. Navigate to Google AI Studio, click on "Get API Key" in the left sidebar, and examine the project column next to your existing API key. If it shows a project that does not have billing enabled, you need to create a new key. Click "Create API key in existing project" and select the specific project where you have billing configured. After generating the new key, update your application to use it and test again. Remember to revoke the old key if it is no longer needed to maintain security hygiene. For a comprehensive guide to fixing Gemini API quota exceeded errors, our resource covers additional troubleshooting steps for persistent 429 errors.
Fix 3: Complete Prepayment Activation and Wait for Sync
If your model variant is correct and your API key is in the right project, the issue may be a billing synchronization delay. First, verify that your billing account is fully active by checking the Google Cloud Console billing page. Ensure there is an active payment method with no pending verification. Then, make a deliberate paid API call using a stable, non-free model to trigger the billing system. After this, wait at least 24 hours before testing again, as some synchronizations take up to 48 hours. During this waiting period, you can monitor your billing dashboard in Google Cloud Console to see if API usage charges begin appearing, which would confirm that the billing linkage is active even if the rate limits have not yet updated.
Fix 4: Address Free Promotional Credits
Check your Google Cloud billing account for any active promotional credits. Navigate to the Billing section in Google Cloud Console and look for any credit balance or promotional offers. If you have active credits from a free trial or promotional campaign, you may need to wait for them to be consumed, or contact Google Cloud support to request that your account be treated as a paid account for tier purposes. Some developers have reported success by explicitly requesting a billing account review from Google support, which can expedite the transition from promotional to full paid status.
Fix 5: Escalate to Google Cloud Support
If none of the above steps resolve the issue, it is time to contact Google Cloud support directly. When filing a support request, include the following information to speed up resolution: your Google Cloud project ID, the specific model variants you are using, your API key identifier (not the key itself), screenshots of your billing page showing active Tier 1 status, and the specific error messages or rate limit headers you are receiving. Reference the numerous forum threads about this issue to demonstrate that it is a known problem. Google support can manually verify and fix the tier assignment on their backend systems, which resolves the issue in cases where the automated synchronization has failed.
How to Verify Your Actual Tier Status
Before assuming you have a tier mismatch, it is critical to verify your actual tier status through multiple independent methods. Relying solely on one indicator can be misleading, as different parts of Google's system may show different information during synchronization periods or configuration changes.
Method 1: Google AI Studio API Keys Page
The most direct way to check your tier is through Google AI Studio. Navigate to the API Keys section and look at the plan column next to your API key. If it shows "Free" when you expect "Pay-as-you-go" or "Tier 1," this confirms a mismatch. Note that the exact label may vary, as Google has changed the naming convention several times. What matters is whether the indicator shows a free or paid designation. If you see "Pay-as-you-go," your project is correctly recognized as Tier 1, and the issue likely lies elsewhere in the chain, such as model variant selection.
Method 2: Google Cloud Console Quotas
Navigate to your Google Cloud Console, select your project, and go to the Quotas and System Limits page. Search for Gemini API or Generative Language API quotas. The displayed limits should reflect your tier level. However, be aware that this page has been reported to sometimes display stale or incorrect information, particularly during the synchronization period after enabling billing. Use this as a supplementary check rather than the sole verification method, and compare what you see here with the AI Studio information from Method 1.
Method 3: API Response Headers
The most reliable real-time verification method is checking the rate limit headers returned with your API responses. When you make a Gemini API request, the response includes headers that indicate your current rate limits and remaining quota. Look for headers like x-ratelimit-limit and x-ratelimit-remaining in the response. If the limit values match free tier numbers (such as 15 RPM or 250 RPD) rather than Tier 1 numbers, you have confirmation that the API is treating your requests as free tier regardless of what your dashboard shows. This method provides ground truth about how the system is actually handling your requests, cutting through any dashboard display inconsistencies.
For Python developers, you can programmatically check your tier status by examining the response headers after any API call. The x-ratelimit-limit-requests-per-day header is the most telling indicator, as the free tier will show values like 100 or 250 depending on the model, while Tier 1 will show 1,500 or higher. You can also check x-ratelimit-limit-requests-per-minute to see your RPM allocation. Building this check into your application startup routine provides an automatic early warning system that catches tier mismatches before they impact your users. Some developers implement a simple health check endpoint that makes a minimal API call on application start, logs the rate limit headers, and alerts if the values do not match the expected tier. This proactive approach is far better than discovering the mismatch only when users start experiencing failures.
Combining all three verification methods gives you a comprehensive picture of your actual tier status. If AI Studio shows "Pay-as-you-go" but the API response headers show free tier limits, the issue is almost certainly model-variant-related. If AI Studio shows "Free" despite billing being enabled, the issue is with project-key linkage or billing synchronization. When all three methods agree that you are on the paid tier but you are still experiencing rate limiting, the problem may be that your actual request volume has legitimately exceeded Tier 1 limits during peak usage, in which case the solution is to optimize your request patterns or work toward Tier 2 qualification. Document your verification results with timestamps, as this information is valuable if you need to escalate to Google Cloud support later, and it helps you track whether any changes you make are having the intended effect on your quota allocation.
Scaling Beyond Tier 1: Higher Limits and Alternatives
Once you have resolved the tier mismatch and confirmed Tier 1 access, you may find that even Tier 1 limits are insufficient for your production workload. Understanding the path to higher tiers and alternative approaches helps you plan capacity effectively without hitting unexpected bottlenecks.
Upgrading from Tier 1 to Tier 2 requires accumulating $250 in cumulative spend on the Gemini API and maintaining an active billing account for at least 30 days since your first payment. This means the upgrade is not instant even if you are willing to spend the money immediately. Google uses the cumulative spend threshold as a trust signal, gradually unlocking higher limits for accounts that demonstrate sustained usage patterns. Tier 3 follows the same principle at the $1,000 cumulative spend threshold. If your project requires immediate high throughput, this ramp-up period can be a significant planning constraint.
Several strategies can help maximize your effective throughput within your current tier. Implementing client-side request batching reduces the number of individual API calls while processing the same volume of data. Aggressive caching of responses for identical or near-identical prompts eliminates redundant API usage entirely. Using the asynchronous batch processing API, where available, allows you to submit large volumes of requests at lower priority with more generous rate limits. Additionally, distributing workloads across multiple Google Cloud projects each with their own billing and tier status can effectively multiply your aggregate capacity, though this adds operational complexity.
For developers who need consistent high-throughput API access without navigating tier restrictions and waiting periods, services like laozhang.ai aggregate multiple AI models with transparent per-request pricing and no rate limit tiers to manage. This can be particularly useful during the ramp-up period while waiting for Tier 2 or Tier 3 qualification, or for applications that need burst capacity exceeding what any single tier provides. The per-request pricing model eliminates the guesswork of tier management and provides predictable cost scaling regardless of usage patterns.
Another approach that production teams commonly employ is implementing a multi-model fallback strategy. Rather than relying exclusively on a single Gemini model at a single tier, you configure your application to cascade between models based on availability and rate limit status. For example, your primary path might use Gemini 2.5 Pro for complex reasoning tasks, with an automatic fallback to Gemini 2.5 Flash when the Pro model's rate limits are approached. Flash models consistently offer higher rate limits at lower cost, making them an excellent fallback for maintaining service availability during high-traffic periods. Some teams take this further by incorporating models from different providers entirely, using API gateway solutions that handle routing across multiple AI providers to ensure their applications remain responsive even when any single provider's rate limits are hit. This architectural pattern of graceful degradation across models and providers has become a best practice for production AI applications that cannot afford downtime due to rate limiting.
FAQ
How long does it take for Tier 1 limits to activate after enabling billing?
Most developers report that Tier 1 limits become active within a few minutes to 24 hours after correctly enabling billing and linking it to their project. However, some cases take up to 48 hours, particularly for new Google Cloud accounts or accounts transitioning from promotional credits to paid billing. If your limits have not updated after 48 hours and you have verified all the root causes discussed in this guide, contact Google Cloud support for manual investigation.
Do free promotional credits count toward Tier 2/Tier 3 upgrade thresholds?
No, free promotional credits do not count toward the cumulative spend thresholds required for Tier 2 ($250) and Tier 3 ($1,000) upgrades. The tier system specifically requires spend from a real payment method. This distinction is important for developers who receive Google Cloud credits through educational programs, startup programs, or promotional offers. Only charges against your actual credit card or billing account accumulate toward tier upgrade requirements.
Why do experimental models have free tier limits even on paid accounts?
Experimental models are intentionally designated as free tier only because they are not yet production-ready and Google wants to limit their usage while gathering feedback and monitoring stability. The -exp suffix in the model name signals that this variant is available at no cost but with free tier rate limits regardless of billing status. This is by design, not a bug, and switching to the equivalent stable or paid preview variant is the intended solution.
Can I increase Gemini API rate limits beyond Tier 3?
For enterprise-scale needs exceeding Tier 3 limits, Google offers the option to request custom quota increases through the Google Cloud Console or by working with Google Cloud sales. You can also access Gemini models through Vertex AI, which provides separate quotas and enterprise-grade features. Custom quota requests are evaluated on a case-by-case basis and may require additional agreements or commitments.
When do RPD quotas reset?
RPD quotas reset at midnight Pacific Time daily. This means if you exhaust your daily quota, you need to wait until 12:00 AM Pacific for the counter to reset. Planning your API usage around this reset time can help optimize throughput for batch processing workloads. Note that RPM limits reset on a rolling per-minute basis, so those recover much more quickly than daily limits.
Is there a way to check my current rate limit usage in real time?
Yes, the most reliable method is examining the rate limit headers in your API responses, specifically x-ratelimit-remaining and x-ratelimit-reset. You can also monitor usage through the Google Cloud Console Quotas page, though this may have slight delays. For programmatic monitoring, building a simple middleware that logs these response headers gives you real-time visibility into your quota consumption and helps you implement proactive rate limiting before hitting the hard limits.
I switched to a stable model but my limits are still showing as free tier. What else should I check?
If you have confirmed that your model variant is correct (no -exp suffix), the most likely remaining cause is the API key linkage. Even experienced developers sometimes overlook this: the API key itself carries the association with a specific Google Cloud project, and that project's billing status determines your tier. Create a completely new API key from within Google AI Studio, making sure to select the project with active billing when prompted. Test with this new key immediately. If the rate limit headers still show free tier values, the issue is almost certainly a billing synchronization delay or promotional credit override, and you should follow Fix 3 and Fix 4 from the step-by-step guide above.
Does switching between Gemini API and Vertex AI affect my tier and rate limits?
Yes, Gemini API (accessed through generativelanguage.googleapis.com) and Vertex AI (accessed through aiplatform.googleapis.com) operate on separate quota systems with different rate limit configurations. Your Gemini API tier status does not automatically transfer to Vertex AI, and vice versa. Vertex AI uses its own quota management system tied to your Google Cloud project and region. If you are hitting rate limits on one endpoint, switching to the other may provide additional capacity, but you will need to configure authentication and billing separately for each. Many production applications use both endpoints strategically, leveraging Gemini API for its simpler setup and Vertex AI for enterprise features like VPC Service Controls and customer-managed encryption keys.
Nano Banana Pro
4K-80%Google Gemini 3 Pro · AI Inpainting
Google Native Model · AI Inpainting