Clawdbot Troubleshooting Guide: Fix Gateway, Authentication, and Connection Errors (2026)
Complete troubleshooting guide for Clawdbot issues including gateway won't start, error 4014, authentication failures, and WhatsApp/Telegram connection problems. Step-by-step fixes with diagnostic commands.
Nano Banana Pro
4K-80%Google Gemini 3 Pro · AI Inpainting
谷歌原生模型 · AI智能修图
When Clawdbot stops working, the frustration is real. You've invested time setting up your personal AI assistant, and now it refuses to start, throws cryptic error codes, or simply won't connect to your messaging platforms. This guide provides systematic solutions for every common Clawdbot issue.
Quick Answer: If your Clawdbot gateway won't start, run clawdbot doctor --fix to auto-repair configuration issues. For authentication errors, use clawdbot models auth setup-token --provider anthropic. For Discord error 4014, enable Message Content Intent in the Discord Developer Portal.
This comprehensive troubleshooting guide covers gateway startup failures, authentication problems, platform-specific connection issues, and advanced debugging techniques. Whether you're running Clawdbot on macOS, Linux, or WSL, you'll find the solution here.
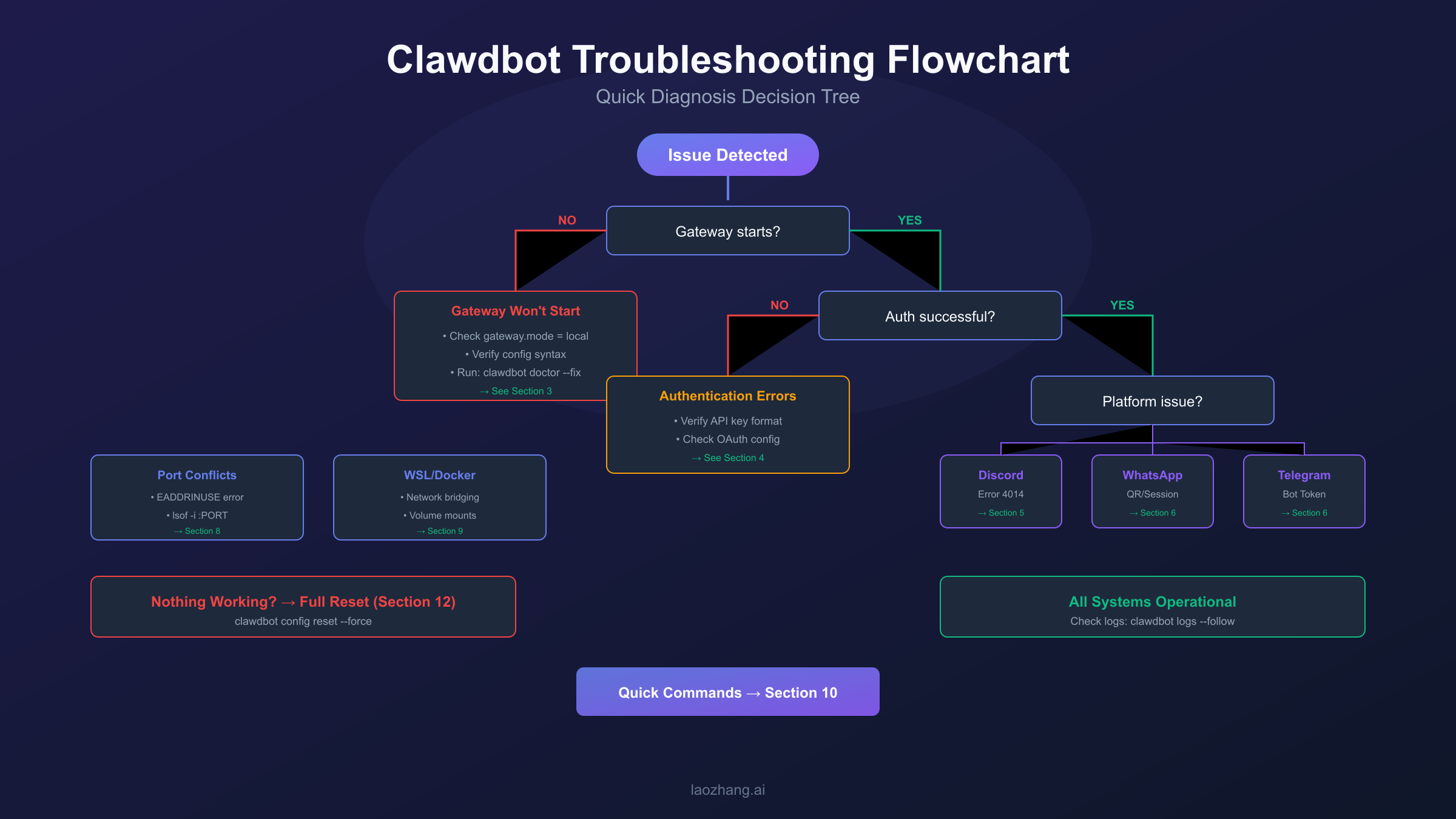
Quick Diagnosis: First 60 Seconds
Before diving into specific fixes, run this rapid diagnostic sequence to identify your issue category. The goal is to narrow down the problem within one minute.
Step 1: Check Gateway Status
hljs bashclawdbot gateway status
This command reveals three critical pieces of information: whether the service is installed, whether it's actually running, and what port it's bound to. If you see "Service: installed" but "Running: false", your gateway failed to start. If "Running: true" but "RPC probe: failed", the gateway is running but not responding—likely a port or binding issue.
Step 2: Run the Doctor
hljs bashclawdbot doctor
The doctor command scans your configuration for invalid entries, missing credentials, and system issues. Pay attention to any red flags—these are blocking problems that must be fixed before the gateway can start. The output categorizes issues by severity, so focus on errors before warnings.
Step 3: Check Recent Logs
hljs bashclawdbot logs --limit 50
The last 50 log lines usually reveal the immediate cause of failure. Look for keywords like "error", "failed", "refused", or "unauthorized". If you see "OAuth token refresh failed", jump to the Authentication section. If you see "4014", go to Discord troubleshooting. If you see "gateway.mode", check the Gateway section.
Quick Reference Decision Tree:
| Symptom | Most Likely Cause | Go To |
|---|---|---|
| "gateway.mode not set" | Configuration missing | Gateway section |
| "No API key found" | Auth not configured | Authentication section |
| "Error 4014" | Discord intents disabled | Discord section |
| "Disconnected (1008)" | Token/pairing issue | Platform section |
| "Address already in use" | Port conflict | Port Conflicts section |
Gateway Won't Start: 5 Common Causes and Fixes
The gateway is Clawdbot's core process—if it won't start, nothing else works. Here are the five most common reasons for gateway startup failures, ordered by frequency.
Cause 1: Gateway Mode Not Configured
This is the single most common reason the gateway refuses to start. When you run clawdbot gateway and nothing happens, check if gateway.mode is set in your configuration. The gateway intentionally won't start without explicit mode configuration as a safety measure.
The fix depends on your setup. For local installations (the most common case), run:
hljs bashclawdbot config set gateway.mode local
If you're connecting to a remote gateway server, configure it with:
hljs bashclawdbot config set gateway.mode remote
clawdbot config set gateway.remote.url "wss://your-gateway-server.com"
Alternatively, if you want to start the gateway just once without permanently setting the mode, use the bypass flag: clawdbot gateway --allow-unconfigured. This is useful for testing but not recommended for production use.
Cause 2: Invalid Configuration Entries
Recent Clawdbot versions strictly validate configuration files and refuse to start if they contain unknown or malformed entries. This often happens after updating Clawdbot when config formats change, or when manually editing the config file with typos.
The doctor command with the fix flag handles this automatically:
hljs bashclawdbot doctor --fix
This scans your configuration, removes invalid entries, and rewrites the config file with correct formatting. After running this, restart the gateway with clawdbot gateway restart. If you use plugins, also run clawdbot plugins update as outdated plugins can introduce invalid config sections.
Cause 3: Missing Configuration File
If you've never run setup or accidentally deleted your config, the gateway has nothing to work with. The fix is straightforward—run the setup wizard:
hljs bashclawdbot setup
This interactive wizard walks you through essential configuration: choosing your AI provider, setting up authentication, and configuring messaging channels. After setup completes, the gateway should start without issues.
Cause 4: Auth Required for Non-Loopback Binding
This catches many users who try to expose Clawdbot on their local network or Tailnet. If you set gateway.bind to lan, tailnet, or custom, Clawdbot requires authentication configuration to prevent unauthorized access. Without auth, you'll see "refusing to bind ... without auth" in logs.
To fix this, configure gateway authentication:
hljs bashclawdbot config set gateway.auth.mode token
clawdbot config set gateway.auth.token "your-secure-token"
Alternatively, export the token as an environment variable: export CLAWDBOT_GATEWAY_TOKEN="your-secure-token". Then restart the gateway. If you only need local access, the simpler solution is to revert to loopback binding: clawdbot config set gateway.bind loopback.
Cause 5: Service Installation Issues
Sometimes the underlying service (launchd on macOS, systemd on Linux) gets into a bad state. The supervisor thinks the process should be running, but it's actually crashed or stuck. Running clawdbot gateway status shows "Service: installed, Running: true" but the actual process isn't there.
Force reinstall the service:
hljs bashclawdbot gateway stop clawdbot gateway uninstall clawdbot gateway install clawdbot gateway start
This sequence completely removes and reinstalls the service configuration, clearing any corrupted state.
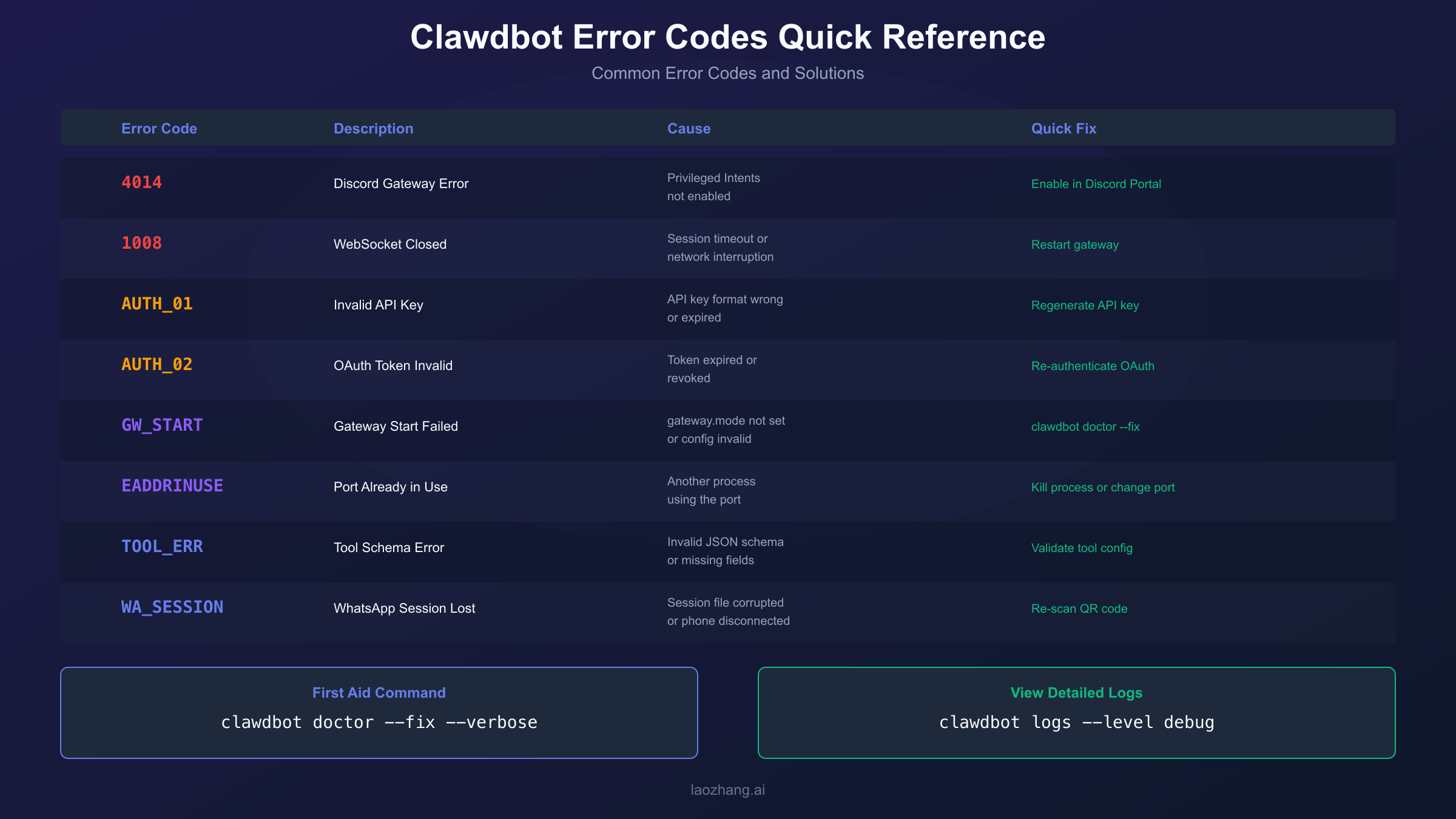
Authentication Errors: API Keys and OAuth
Authentication problems manifest in several ways: "No API key found for provider anthropic", "OAuth token refresh failed", or simply the model refusing to respond. Understanding the authentication architecture helps you fix these issues quickly.
Understanding Clawdbot's Auth System
Clawdbot supports two authentication methods for Claude: OAuth (using your Claude Pro/Max subscription) and API keys (direct Anthropic API access). These are stored per-agent, meaning each agent you create needs its own authentication configured. This is intentional—different agents might use different providers or accounts.
Fix: Missing API Key
If you see "No API key found for provider anthropic", the current agent has no credentials configured. The easiest fix is re-running the provider setup:
hljs bashclawdbot models auth setup-token --provider anthropic
This prompts you to enter your Anthropic API key or Claude setup token. For API keys, paste your key directly. For Claude subscriptions, you'll need to generate a setup token from Claude Code settings and paste it when prompted.
Alternatively, if you have another agent with working authentication, you can copy its credentials:
hljs bashcp ~/.clawdbot/agents/working-agent/auth-profiles.json ~/.clawdbot/agents/broken-agent/
Fix: OAuth Token Expired
Claude subscription authentication uses OAuth tokens that expire and need refreshing. When refresh fails (network issues, subscription lapsed, etc.), you'll see "OAuth token refresh failed". The most reliable fix is switching to setup tokens, which don't require refresh:
hljs bashclawdbot models auth setup-token --provider anthropic
When prompted, choose "Claude Code setup-token" and paste a fresh token from your Claude Code settings. This authentication method is more robust for long-running gateway instances.
Fix: Token Mismatch Between Gateway and CLI
If your CLI works but the gateway can't authenticate, there might be a token configuration mismatch. This happens when gateway.remote.token and gateway.auth.token have different values. Verify they match:
hljs bashclawdbot config get gateway.remote.token clawdbot config get gateway.auth.token
If they differ, set them to the same value and restart the gateway.
For those using API aggregation platforms like laozhang.ai for Claude API access (which offers multi-node stability and unified billing), the integration is straightforward since these platforms are OpenAI-compatible. However, for native Clawdbot Claude integration, direct Anthropic authentication is required. More details on Claude API configuration can be found in our Claude API error code guide.
Discord Error 4014: Enabling Privileged Intents
Error 4014 is Discord-specific and extremely common among new Clawdbot users. It means your Discord bot is trying to use privileged gateway intents that haven't been enabled in the Discord Developer Portal. The gateway won't start until this is fixed.
Why This Happens
Discord requires explicit opt-in for certain sensitive capabilities like reading message content. When Clawdbot tries to connect without these permissions, Discord rejects the connection with error 4014. This is a Discord platform requirement, not a Clawdbot bug.
Step-by-Step Fix
First, navigate to the Discord Developer Portal at discord.com/developers and log in with the account that owns the bot.
Select your Clawdbot application from the application list. In the left sidebar, click "Bot" to access bot settings.
Scroll down to the "Privileged Gateway Intents" section. You'll see three toggles:
- PRESENCE INTENT - Optional. Enable if you want Clawdbot to see user presence status.
- SERVER MEMBERS INTENT - Optional. Enable if you need member information in servers.
- MESSAGE CONTENT INTENT - Required. This is the critical one. Without this, Clawdbot cannot read messages and will fail with error 4014.
Toggle MESSAGE CONTENT INTENT to ON. Click "Save Changes" at the bottom of the page.
Verify the Fix
Return to your terminal and restart the Clawdbot gateway:
hljs bashclawdbot gateway restart
Check the status:
hljs bashclawdbot status --deep
The Discord channel should now show "connected" instead of "4014". If you still see errors, wait 5-10 minutes for Discord's cache to update, then try again.
Common Mistake
Some users enable intents on one bot but have their Clawdbot configured with a different bot token. Verify you're editing the correct application by checking that the Application ID in the Developer Portal matches your configured bot. Run clawdbot config get channels.discord.token to see your configured token and compare.
WhatsApp and Telegram Connection Issues
Platform connection problems are frustrating because they can have many causes—from network issues to authentication problems to platform-specific quirks. Here's how to systematically diagnose and fix them.
Diagnosing Connection Status
Start with a deep status check:
hljs bashclawdbot status --deep
This probes each configured channel and reports its actual connection state. Look for channels showing "disconnected" or "error" status.
For more detailed connection event history:
hljs bashclawdbot logs --limit 200 | grep "connection\|disconnect\|logout"
This filters logs to show only connection-related events, helping you identify when and why disconnections occurred.
WhatsApp: Session Lost or Logged Out
WhatsApp connections can drop when the session becomes invalid—often because WhatsApp Web was used elsewhere, or the phone was offline too long. Symptoms include "disconnected" status or "pairing required" errors.
To re-establish the connection:
hljs bashclawdbot channels logout
clawdbot channels login --verbose
The verbose flag shows the QR code in your terminal. Scan it with WhatsApp on your phone (Settings → Linked Devices → Link a Device). The connection should establish within seconds.
WhatsApp: Self-Chat Not Working
If you're trying to message yourself (a common Clawdbot use case) and it's not working, you need to explicitly enable self-chat mode. Edit your config to include:
hljs json{
"channels": {
"whatsapp": {
"selfChatMode": true,
"allowFrom": ["+your-phone-number"]
}
}
}
Replace +your-phone-number with your actual number including country code. Restart the gateway after this change.
Telegram: Bot Not Responding
Telegram issues usually stem from bot token problems or missing bot username configuration. Verify your bot token is correct:
hljs bashclawdbot config get channels.telegram.token
If the token looks corrupted or you're unsure, generate a new one from BotFather on Telegram and update the configuration:
hljs bashclawdbot configure --section telegram
This runs the Telegram setup wizard with your existing settings, letting you update the token.
Both Platforms: Network Issues
If both WhatsApp and Telegram fail to connect, the issue might be network-level. Test basic connectivity:
hljs bash# If running in Docker:
docker exec clawdbot ping -c 3 8.8.8.8
If pings fail, check your firewall (UFW on Linux) allows outbound connections. On WSL, ensure Windows Defender isn't blocking the WSL network interface.
Node.js Runtime Requirement
WhatsApp and Telegram channels specifically require Node.js—Bun is not supported for these channels due to dependencies on native modules. If you installed Clawdbot with Bun, run clawdbot doctor to identify the issue and follow its guidance to migrate to a system Node installation.
Tool Schema Errors and Cloud Code Assist
If you see errors mentioning "invalid tool schema" or "Cloud Code Assist API error (400)", you've hit a compatibility issue with the Claude API's strict JSON Schema requirements. This commonly affects users with custom tools or those using certain MCP servers.
Understanding the Issue
The Claude API (specifically the Cloud Code Assist endpoint) only accepts a subset of JSON Schema. Keywords that work in standard JSON Schema validation may be rejected by Claude. Clawdbot includes a schema scrubber in recent versions that normalizes tool schemas, but if you're running an older release, you'll hit these errors.
Quick Fix: Update Clawdbot
The simplest solution is updating to the latest version:
hljs bashnpm update -g clawdbot
# or if using pnpm:
pnpm update -g clawdbot
Then restart the gateway. The built-in schema scrubber should handle most compatibility issues automatically.
Running from Source
If you're running from source and can't wait for a release, pull the latest main branch:
hljs bashcd ~/clawdbot
git pull origin main
pnpm install
pnpm build
clawdbot gateway restart
Avoid Unsupported Schema Keywords
If you're defining custom tools, avoid these unsupported JSON Schema keywords:
anyOf,oneOf,allOf- Use simpler type definitionspatternProperties- Use explicit property namesadditionalProperties- Remove or use explicit propertiesminLength,maxLength- Remove string constraintsformat- Remove format specifications
Keep your tool schemas simple: use type: "object" at the top level with explicit properties and simple enums. Complex nested schemas cause problems.
Port Conflicts and Gateway Binding Issues
Port conflicts prevent the gateway from starting even when everything else is configured correctly. You'll see "Address already in use" errors or the gateway reporting it's running but nothing listening on the expected port.
Identifying the Conflict
Check what's currently listening on the Clawdbot port (default 18789):
hljs bash# macOS and Linux:
lsof -nP -iTCP:18789 -sTCP:LISTEN
# Alternative on Linux:
ss -tlnp | grep 18789
This shows the process ID and name of whatever is using the port. Common culprits include another Clawdbot instance, a previous gateway that didn't shut down cleanly, or another application using the same port.
Fix: Kill the Conflicting Process
If it's a zombie Clawdbot process:
hljs bashclawdbot gateway stop
# If that doesn't work:
pkill -f clawdbot
Then restart: clawdbot gateway start.
If another application needs the port, change Clawdbot's port instead:
hljs bashclawdbot config set gateway.port 18790
clawdbot gateway restart
Tailnet Binding Issues
If you've configured Tailscale binding (gateway.bind: tailnet) but Tailscale isn't running, the gateway fails to start because it can't find an IP in the 100.64.0.0/10 range.
Either start Tailscale on the machine, or change binding to loopback:
hljs bashclawdbot config set gateway.bind loopback
clawdbot gateway restart
WSL and Docker Troubleshooting
Running Clawdbot in WSL or Docker introduces platform-specific challenges. This section covers the most common issues in these environments.
WSL: Prerequisites and Setup
Windows users must use WSL2—WSL1 and native Windows are not supported. If you haven't enabled WSL2 properly, you'll hit various issues.
From an Administrator PowerShell, run:
hljs powershelldism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
Reboot after these commands. Then set WSL2 as default:
hljs powershellwsl --set-default-version 2
WSL: Error 1008 "Pairing Required"
This error in WSL Docker deployments indicates session issues. The fix involves resetting the pairing:
hljs bashclawdbot channels logout
rm -rf ~/.clawdbot/credentials/
clawdbot channels login
Scan the QR code again to re-establish the session.
Docker: Memory Issues
Running Clawdbot on small VMs (1GB RAM) often fails during npm install with out-of-memory errors. The solution is adding swap space:
hljs bashsudo fallocate -l 2G /swapfile
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile
sudo mkswap /swapfile
sudo swapon /swapfile
Then retry the installation.
Docker: Sandbox Environment Variables
Skills that work on the host but fail in sandbox with "missing API key" errors happen because Docker containers don't inherit host environment variables. Configure environment passthrough in your Clawdbot config:
hljs json{
"agents": {
"defaults": {
"sandbox": {
"docker": {
"env": ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY", "OTHER_KEY"]
}
}
}
}
}
After updating, recreate the sandbox:
hljs bashclawdbot sandbox recreate --agent <agent-id>
Docker: Browser/Chromium Issues on Linux
If browser automation fails with "CDP port 18800 error", it's likely because snap-packaged Chromium doesn't work properly with Clawdbot's automation.
Install Google Chrome directly:
hljs bashwget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
sudo apt-get install -f
Then configure Clawdbot to use it:
hljs bashclawdbot config set browser.executablePath "/usr/bin/google-chrome-stable"
Essential Diagnostic Commands Reference
Having the right commands at your fingertips accelerates troubleshooting. Here's a comprehensive reference of the most useful diagnostic commands.
Status Commands
| Command | Purpose | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
clawdbot status | Quick overview of gateway, agents, providers | First diagnostic step |
clawdbot status --deep | Full probe including channel connectivity | When basic status shows OK but things don't work |
clawdbot status --all | Complete diagnosis with redacted logs | When sharing with others for help |
clawdbot gateway status | Service state, PID, port, config paths | Gateway-specific issues |
clawdbot gateway status --deep | System-level scans included | Deep gateway investigation |
Health and Connectivity
| Command | Purpose | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
clawdbot health --json | JSON gateway reachability check | Scripting/automation |
clawdbot health --verbose | Detailed connection information | RPC connectivity issues |
clawdbot gateway probe | Discovery + reachability test | Suspect wrong gateway target |
clawdbot channels status --probe | Channel status with probes | Gateway OK but channels broken |
Logs and Diagnostics
| Command | Purpose | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
clawdbot logs --follow | Live log stream | Real-time monitoring |
clawdbot logs --limit 200 | Recent log entries | Post-mortem analysis |
clawdbot doctor | Report config and system issues | Configuration problems |
clawdbot doctor --fix | Auto-repair configuration | After identifying config issues |
Model and Auth
| Command | Purpose | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
clawdbot models status | Verify provider credentials | Auth problems |
clawdbot models list | Show supported models | Model selection |
clawdbot models scan | Discover available models | Verify model support |
clawdbot models auth setup-token --provider anthropic | Configure authentication | Auth setup/reset |

Prevention Tips and Best Practices
While troubleshooting skills are valuable, preventing issues is better. These practices reduce the likelihood of Clawdbot problems.
Keep Clawdbot Updated
Many issues stem from running outdated versions. Check for updates regularly:
hljs bashnpm outdated -g clawdbot
Update when new versions are available: npm update -g clawdbot. New releases often include fixes for known issues and improved compatibility.
Monitor Gateway Health
Set up periodic health checks. A simple cron job can alert you to problems before they become critical:
hljs bash# Add to crontab:
*/5 * * * * clawdbot health --json | grep -q '"healthy":true' || echo "Clawdbot unhealthy" | mail -s "Alert" [email protected]
Back Up Your Configuration
Before making changes, back up your config:
hljs bashcp ~/.clawdbot/moltbot.json ~/.clawdbot/moltbot.json.backup
This lets you quickly revert if changes cause problems.
Use Stable Authentication
OAuth tokens expire and require refresh. For production deployments, setup tokens are more reliable:
hljs bashclawdbot models auth setup-token --provider anthropic
Refresh your setup token periodically (monthly is a good cadence) before it expires.
Document Your Setup
Keep notes on your specific configuration, especially any custom settings. When troubleshooting, you'll know what's intentional versus potentially problematic.
Nuclear Option: Full Reset and Clean Reinstall
When nothing else works and you want a completely fresh start, the nuclear option removes all state and requires reconfiguring from scratch. Use this as a last resort.
Warning: This deletes all sessions, credentials, and configuration. You'll need to re-pair WhatsApp, reconfigure all channels, and set up authentication again.
Full Reset Procedure
hljs bash# Stop everything
clawdbot gateway stop
clawdbot gateway uninstall
# Remove all state
rm -rf ~/.clawdbot
# Reinstall
npm install -g clawdbot
# Fresh setup
clawdbot setup
clawdbot channels login
clawdbot gateway install
clawdbot gateway start
After the reset, verify everything works:
hljs bashclawdbot status --deep
Partial Reset Alternative
If you only want to reset specific components, you can target them individually:
- Reset channels only:
rm -rf ~/.clawdbot/credentials && clawdbot channels login - Reset config only:
rm ~/.clawdbot/moltbot.json && clawdbot setup - Reset specific agent:
rm -rf ~/.clawdbot/agents/<agent-id>
These partial resets preserve other state, reducing reconfiguration effort.
FAQ: Clawdbot Troubleshooting Questions
Q1: My gateway shows "Running" but Clawdbot doesn't respond. What's wrong?
This usually means the gateway is running but not properly connected to your messaging channels. Run clawdbot status --deep to check channel connectivity. Also verify your allowFrom configuration—if the sender isn't allowlisted, messages are ignored silently.
Q2: I updated Clawdbot and now it won't start. How do I fix this?
Updates sometimes change configuration formats. Run clawdbot doctor --fix to repair any incompatible settings. If that doesn't work, check the release notes for breaking changes that require manual migration.
Q3: Can I run multiple Clawdbot instances on the same machine?
Yes, but each instance needs a unique port and state directory. Use environment variables: CLAWDBOT_STATE_DIR=~/.clawdbot-2 clawdbot gateway --port 18790. Configure each instance separately.
Q4: My messages aren't triggering responses in group chats. Why?
Group chats typically require mentions by default. Check your mentionPatterns configuration and ensure you're @mentioning the bot correctly. Alternatively, set channels.discord.groupPolicy: "open" for Discord or adjust requireMention settings for other platforms.
Q5: How do I get help if this guide doesn't solve my problem?
Post in GitHub Discussions with the output of clawdbot status --all (it's automatically redacted for safety). Include your Clawdbot version, operating system, and specific error messages. The community is generally responsive and helpful.
For related troubleshooting on Claude API issues, see our Claude API quota and limits guide. If you're experiencing general API connectivity issues, the Claude API error code reference covers HTTP status codes and their solutions.