- 首页
- /
- 博客
- /
- API Troubleshooting
- /
- Nano Banana Pro API Returns Text Instead of Image: Complete Fix Guide (2025)
Nano Banana Pro API Returns Text Instead of Image: Complete Fix Guide (2025)
Fix the common issue where Nano Banana Pro returns text instead of images. Learn about responseModalities configuration, proper response parsing, and troubleshooting steps.
Nano Banana Pro
4K-80%Google Gemini 3 Pro · AI Inpainting
谷歌原生模型 · AI智能修图
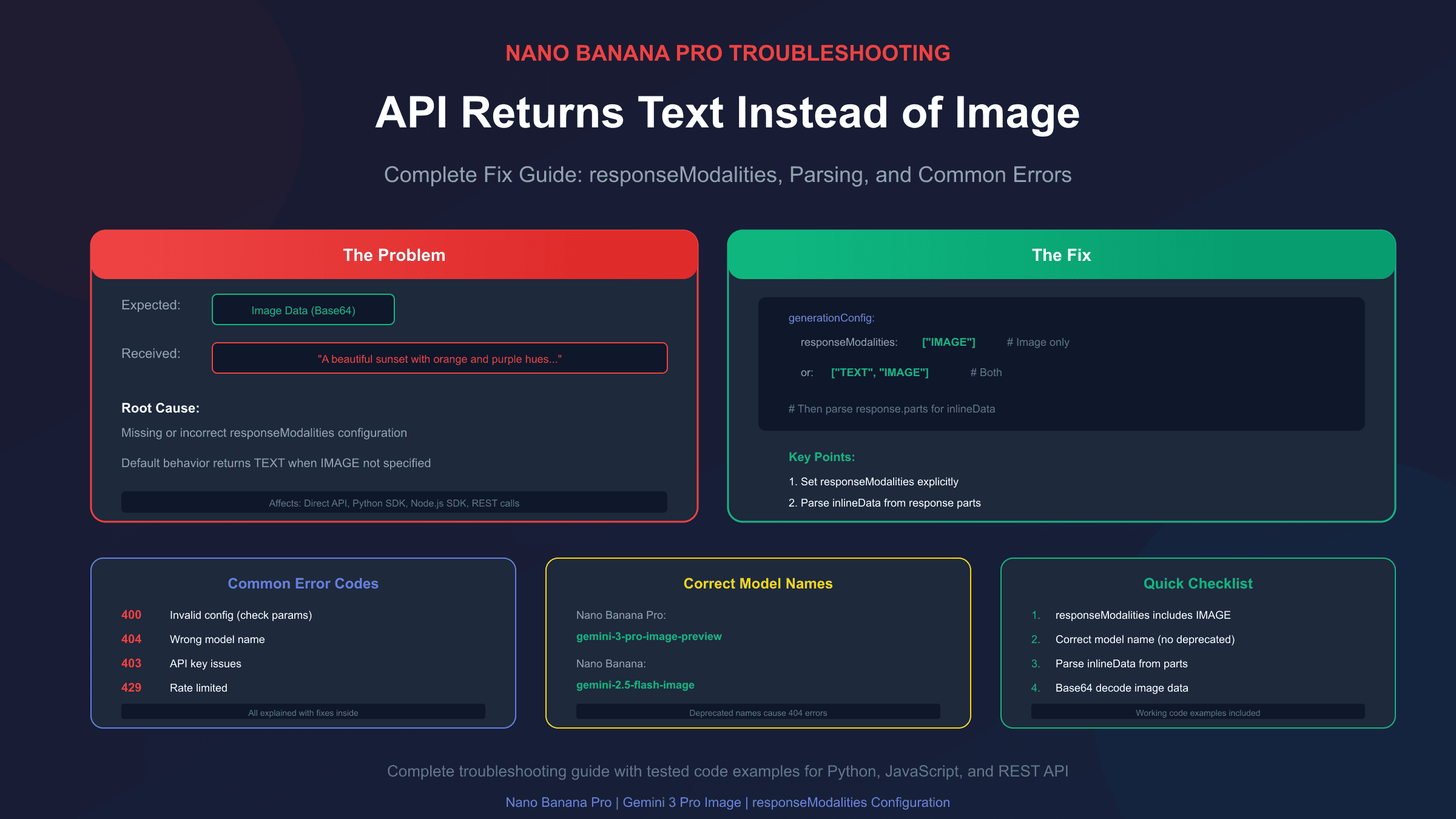
You've set up your Nano Banana Pro API call, crafted the perfect prompt, and hit send—only to receive a text description of what the image should look like instead of an actual image. This frustrating issue has affected countless developers working with Google's Gemini image generation models, and the root cause is almost always a configuration problem.
The primary culprit is the responseModalities parameter in your generationConfig. When this parameter is missing, incorrectly formatted, or set to ["TEXT"] only, the API defaults to returning text responses. The fix is straightforward once you understand what's happening, but the devil is in the details of implementation across different SDKs and API versions.
This guide walks through every reason why Nano Banana Pro might return text instead of images, provides working code examples for each scenario, and covers the common gotchas that trip up even experienced developers. If you're new to Nano Banana Pro, see our complete API guide first.
Understanding Why This Happens
Before diving into fixes, it's worth understanding the architecture. Nano Banana Pro (the Gemini 3 Pro Image model, model ID gemini-3-pro-image-preview) is a multimodal model capable of generating both text and images. Unlike dedicated image models that only output images, Nano Banana Pro can respond with text descriptions, images, or both—depending on how you configure your request.
The responseModalities parameter tells the model which output types you want. According to Google's official documentation, when this parameter is not defined or empty, the model defaults to returning only text. This is the single most common cause of the "text instead of image" problem.
There are three main scenarios where you'll encounter this issue:
- Missing
responseModalitiesentirely: The parameter isn't included in your request - Incorrect value for
responseModalities: Set to["TEXT"]instead of including"IMAGE" - Response parsing error: The image is actually in the response, but your code isn't extracting it correctly
Let's examine each scenario with concrete fixes.
The Primary Fix: Setting responseModalities Correctly
The most common fix is simply adding or correcting the responseModalities parameter. Here's the correct configuration for different scenarios:
For Image-Only Output
If you want only images with no accompanying text:
hljs pythonfrom google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-pro-image-preview",
contents="A photorealistic mountain landscape at sunset",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
response_modalities=["IMAGE"] # Image only, no text
)
)
For Mixed Text and Image Output
If you want both text and images (the model's default behavior when properly configured):
hljs pythonresponse = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-pro-image-preview",
contents="Create an image of a futuristic city and describe it",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
response_modalities=["TEXT", "IMAGE"] # Both modalities
)
)
REST API Format
When making direct HTTP requests:
hljs json{
"contents": [{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{"text": "A cute robot in a garden"}]
}],
"generationConfig": {
"responseModalities": ["TEXT", "IMAGE"]
}
}
Note the capitalization: responseModalities uses camelCase in REST requests, while Python SDK uses snake_case (response_modalities). This inconsistency has caused many debugging headaches.
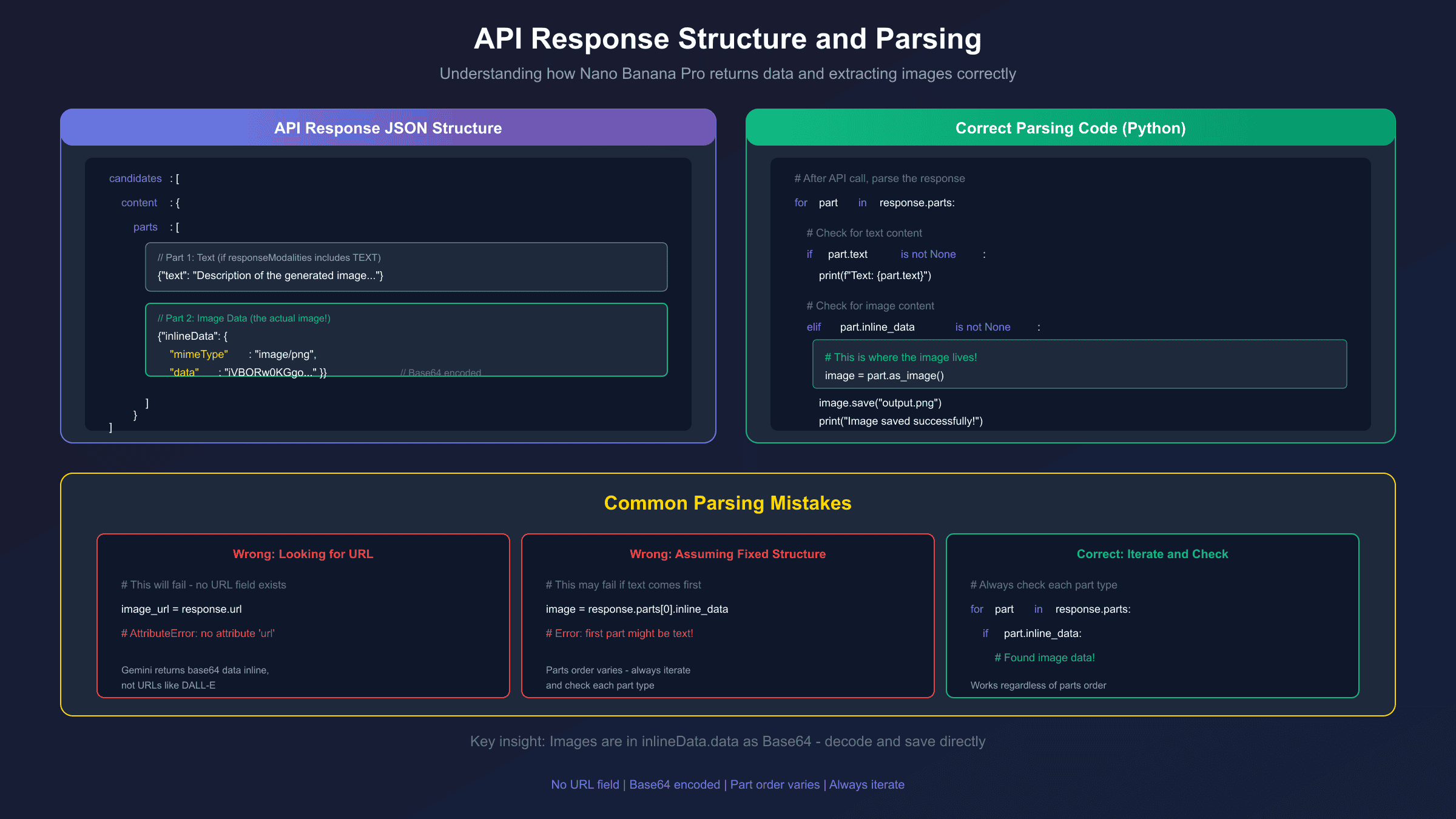
Properly Parsing the Response
Even with correct configuration, you won't see images if your code doesn't parse the response correctly. The Gemini API response structure contains parts that can include text, images, or both. Here's how to handle each:
Python SDK Response Parsing
hljs pythonfor part in response.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(f"Text: {part.text}")
elif part.inline_data is not None:
# This is the image data
image = part.as_image()
image.save("generated_image.png")
print("Image saved successfully")
JavaScript/Node.js Response Parsing
hljs javascriptconst response = await model.generateContent(prompt);
for (const part of response.response.candidates[0].content.parts) {
if (part.text) {
console.log("Text:", part.text);
} else if (part.inlineData) {
// Image is base64 encoded
const imageData = part.inlineData.data;
const buffer = Buffer.from(imageData, "base64");
fs.writeFileSync("output.png", buffer);
console.log("Image saved");
}
}
Raw REST API Response Parsing
hljs pythonimport requests
import base64
response = requests.post(api_url, headers=headers, json=payload)
result = response.json()
# Navigate the response structure
for part in result["candidates"][0]["content"]["parts"]:
if "text" in part:
print(part["text"])
elif "inlineData" in part:
image_data = part["inlineData"]["data"]
mime_type = part["inlineData"]["mimeType"] # Usually image/png
with open("output.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(base64.b64decode(image_data))
The key insight: images are returned as base64-encoded data within inlineData, not as URLs. If you're looking for a URL field, you won't find it—you need to decode the base64 data directly.
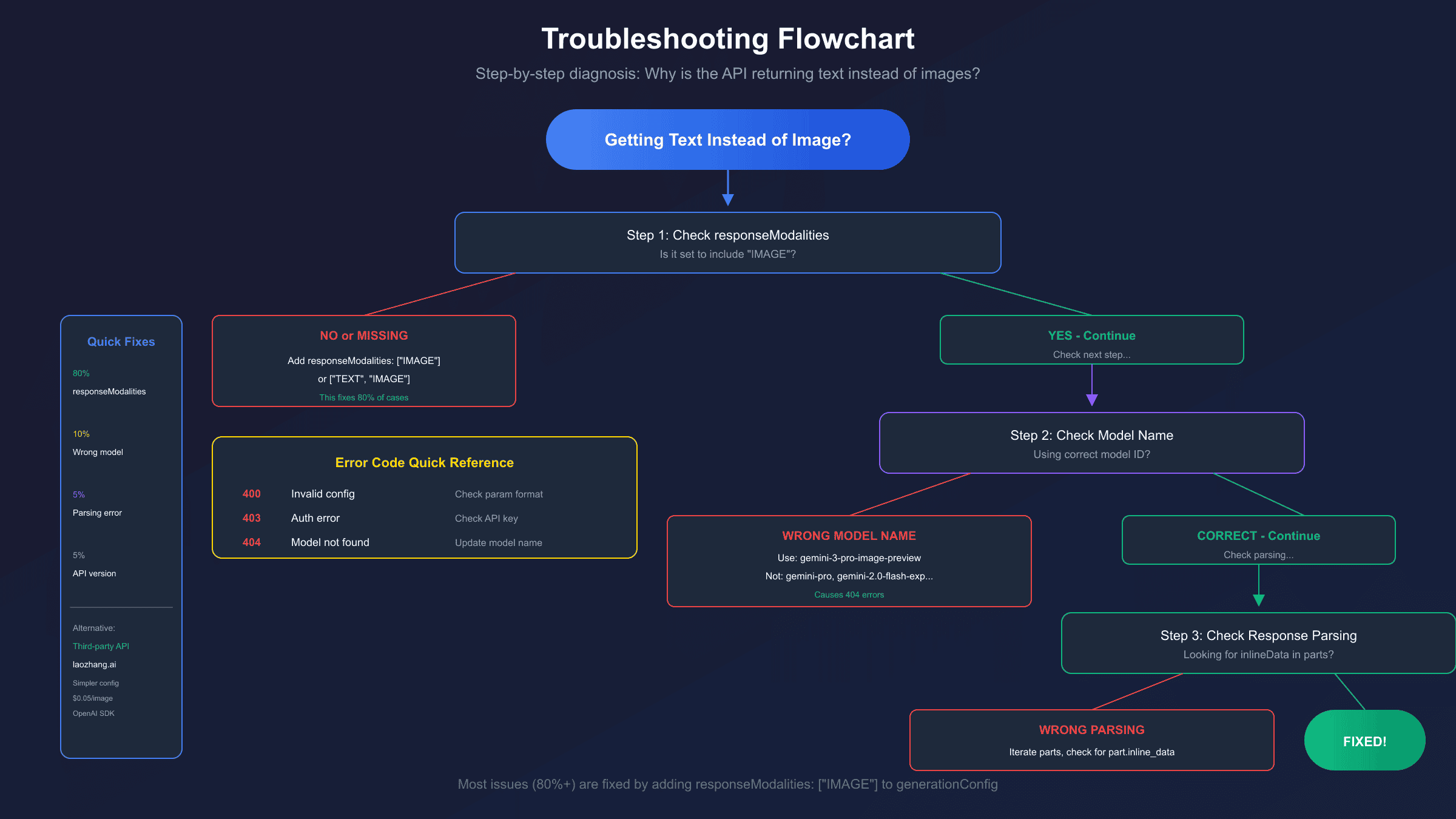
Common Error Codes and Their Meanings
Beyond the text-instead-of-image issue, several errors can prevent image generation entirely. Understanding these helps diagnose problems faster.
400 Bad Request
A 400 error indicates invalid request parameters. Common causes include:
| Cause | Fix |
|---|---|
Mixed thinking_budget and thinking_level | Use only one parameter, not both |
Invalid aspectRatio value | Use supported ratios: 1:1, 3:2, 4:3, 16:9, etc. |
| Malformed JSON | Validate JSON structure before sending |
| Unsupported parameter for model | Remove parameters not supported by image models |
404 Not Found
The 404 error almost always means incorrect model name. As noted in the Gemini troubleshooting guide:
# Wrong (deprecated or incorrect model names)
gemini-pro
gemini-2.0-flash-exp-image-generation
gemini-pro-image
# Correct model names (as of December 2025)
gemini-3-pro-image-preview # Nano Banana Pro
gemini-2.5-flash-image # Nano Banana
gemini-2.0-flash # Standard Gemini without image gen
To check available models:
hljs bashcurl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models?key=YOUR_API_KEY"
403 Forbidden
Usually indicates API key issues:
- Key doesn't have permission for image generation
- Key is restricted to specific APIs
- Quota exceeded
429 Rate Limited
You've hit rate limits. For free tier users, Gemini 2.5 Pro allows only 5 requests per minute. Consider implementing exponential backoff or upgrading to a paid tier.
Model Name Confusion: A Complete Reference
The naming confusion around Gemini image models trips up many developers. Here's a definitive reference:
| Common Name | Official Model ID | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Nano Banana Pro | gemini-3-pro-image-preview | Active (current) |
| Nano Banana | gemini-2.5-flash-image | Active |
| — | gemini-2.0-flash-exp-image-generation | Deprecated Oct 2025 |
| — | gemini-2.0-flash-preview-image-generation | Deprecated Oct 2025 |
The "Nano Banana" naming comes from Google's internal codename. When searching for documentation, search for both "Nano Banana Pro" and "gemini-3-pro-image" to find all relevant resources.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Checklist
When you're getting text instead of images, work through this checklist:
-
Verify
responseModalitiesis set- Must include
"IMAGE"(either alone or with"TEXT") - Check spelling and capitalization for your SDK
- Must include
-
Confirm correct model name
- Use
gemini-3-pro-image-previewfor Nano Banana Pro - Avoid deprecated model names
- Use
-
Check API version
- Image generation requires
/v1betaendpoint - The
/v1endpoint may not support all features
- Image generation requires
-
Validate your prompt
- Explicitly request image generation: "Generate an image of..."
- Avoid prompts that sound like they're asking for descriptions
-
Parse response correctly
- Check both
textandinlineDataparts - Base64 decode the image data
- Don't look for URL fields—images are inline
- Check both
-
Review error responses
- Log the full API response, not just the error message
- Check for
candidates[0].finishReasonvalues likeSAFETYorRECITATION
Working Complete Example
Here's a complete, tested example that handles all edge cases:
hljs pythonimport base64
import requests
from pathlib import Path
def generate_image_with_nano_banana_pro(
prompt: str,
api_key: str,
output_path: str = "output.png",
aspect_ratio: str = "1:1",
image_only: bool = True
) -> dict:
"""
Generate an image using Nano Banana Pro API.
Args:
prompt: The image generation prompt
api_key: Your Gemini API key
output_path: Where to save the generated image
aspect_ratio: Image aspect ratio (1:1, 16:9, 4:3, etc.)
image_only: If True, request only image output
Returns:
dict with 'success', 'image_path', and optional 'text'
"""
url = "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-pro-image-preview:generateContent"
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"x-goog-api-key": api_key
}
# Set responseModalities based on preference
modalities = ["IMAGE"] if image_only else ["TEXT", "IMAGE"]
payload = {
"contents": [{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{"text": f"Generate an image: {prompt}"}]
}],
"generationConfig": {
"responseModalities": modalities,
"imageConfig": {
"aspectRatio": aspect_ratio
}
}
}
try:
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload, timeout=180)
response.raise_for_status()
result = response.json()
# Parse response
output = {"success": False, "image_path": None, "text": None}
if "candidates" not in result or not result["candidates"]:
return {"success": False, "error": "No candidates in response"}
parts = result["candidates"][0]["content"]["parts"]
for part in parts:
if "text" in part:
output["text"] = part["text"]
elif "inlineData" in part:
image_data = part["inlineData"]["data"]
image_bytes = base64.b64decode(image_data)
Path(output_path).write_bytes(image_bytes)
output["image_path"] = output_path
output["success"] = True
return output
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:
return {"success": False, "error": f"HTTP {e.response.status_code}: {e.response.text}"}
except Exception as e:
return {"success": False, "error": str(e)}
# Usage
result = generate_image_with_nano_banana_pro(
prompt="A serene Japanese garden with a koi pond",
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
output_path="garden.png",
aspect_ratio="16:9"
)
if result["success"]:
print(f"Image saved to: {result['image_path']}")
else:
print(f"Error: {result.get('error', 'Unknown error')}")
This example:
- Uses the correct model name and endpoint
- Sets
responseModalitiesproperly - Handles both text and image parts
- Includes proper error handling
- Supports configurable aspect ratios
Third-Party API Solutions
If you're consistently having issues with the official API—whether due to configuration complexity, rate limits, or regional restrictions—third-party API providers offer an alternative approach. Services like laozhang.ai provide access to Nano Banana Pro through a simplified interface.
The main advantages of this approach:
- OpenAI-compatible SDK: Use familiar patterns if you're coming from DALL-E
- Simplified configuration: Less room for configuration errors
- Cost efficiency: Approximately $0.05 per image vs $0.134+ direct
- No daily limits: Pay-per-use model without quota restrictions
Here's how the same image generation looks with a third-party API:
hljs pythonfrom openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key="your-laozhang-key",
base_url="https://api.laozhang.ai/v1"
)
response = client.images.generate(
model="nano-banana-pro",
prompt="A serene Japanese garden with a koi pond",
size="2048x2048",
quality="hd"
)
# Direct URL access - no base64 decoding needed
image_url = response.data[0].url
print(f"Image URL: {image_url}")
The trade-off is trusting a third-party service, but for developers who want to avoid configuration headaches and focus on building, this can be a practical solution. For production workloads where official API costs become significant, the savings compound quickly.
Advanced Configuration Options
Beyond the basic fixes, Nano Banana Pro supports several configuration options that affect output:
Image Resolution
hljs json{
"generationConfig": {
"responseModalities": ["IMAGE"],
"imageConfig": {
"imageSize": "2K" // Options: "1K", "2K", "4K"
}
}
}
Higher resolutions take longer to generate and may be subject to different rate limits. For a complete breakdown of resolution options, see our 4K generation guide.
Aspect Ratios
Supported values: 1:1, 3:2, 2:3, 3:4, 4:3, 4:5, 5:4, 9:16, 16:9, 21:9
hljs pythonconfig=types.GenerateContentConfig(
response_modalities=["IMAGE"],
image_config=types.ImageConfig(
aspect_ratio="16:9"
)
)
Handling Safety Filters
If your prompt is being blocked by safety filters, you may receive text explaining why instead of an image. Check the finishReason in your response:
hljs pythonfinish_reason = result["candidates"][0].get("finishReason")
if finish_reason == "SAFETY":
print("Prompt was blocked by safety filters")
elif finish_reason == "RECITATION":
print("Response blocked due to potential copyright issues")
Debugging Tips for Persistent Issues
When standard fixes don't work, try these debugging approaches:
Log Full Responses
Always log the complete API response, not just the parts you expect:
hljs pythonimport json
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload)
print(json.dumps(response.json(), indent=2))
This reveals unexpected fields, error messages, or structural differences you might miss.
Test with Minimal Configuration
Strip your request down to the absolute minimum that should work:
hljs python# Minimal working request
payload = {
"contents": [{"parts": [{"text": "Generate an image of a red apple"}]}],
"generationConfig": {"responseModalities": ["IMAGE"]}
}
If this works but your full configuration doesn't, add parameters back one at a time to identify the problem.
Compare SDK vs REST
If using an SDK, try the same request via direct REST API. SDKs sometimes have bugs or version-specific issues that a direct HTTP request avoids.
Check Regional Availability
Some image generation features may not be available in all regions. If you're outside the US, try routing through a US-based endpoint or check Google's documentation for regional restrictions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does setting responseModalities to IMAGE sometimes still return text?
Nano Banana Pro uses a "thinking" process internally. In some cases, the model may return its reasoning as text before or alongside the image. If you're only getting text, the most likely cause is still incorrect configuration—but if you're getting text with an image, that's expected behavior for certain prompts.
Can I force the model to never return any text?
Setting responseModalities: ["IMAGE"] (without "TEXT") should theoretically return only images. However, the model may still include brief text in some scenarios. For truly text-free output, parse the response and only save the inlineData parts.
Why does my request work locally but fail in production?
Common causes include:
- Environment variable issues (API key not properly set)
- Network restrictions or firewall rules
- Different library versions between environments
- Region-based restrictions (some features limited to US)
Is there a way to validate my request before sending?
Use Google's AI Studio to test prompts interactively. If it works there but not in your code, the issue is in your implementation, not the prompt or model.
How long should I set the timeout for image generation?
Image generation takes significantly longer than text generation. Set timeout to at least 120-180 seconds for standard images, longer for 4K resolution.
Conclusion
The "text instead of image" issue with Nano Banana Pro almost always comes down to one of three things: missing responseModalities configuration, incorrect parameter values, or improper response parsing. By setting responseModalities: ["IMAGE"] (or ["TEXT", "IMAGE"] for mixed output) and correctly parsing the inlineData field from the response, you should resolve the issue.
For developers who want to avoid configuration complexity entirely, third-party APIs like laozhang.ai provide a simpler interface with OpenAI-compatible SDK patterns—letting you focus on your application logic rather than debugging API configurations.
The key takeaway: always verify your generationConfig includes the correct responseModalities setting, use the current model name (gemini-3-pro-image-preview), and parse responses by iterating through parts rather than assuming a specific structure. With these fundamentals in place, Nano Banana Pro becomes a reliable image generation tool.