How to Check Nano Banana Pro API Quota & Usage in Google Cloud (2025 Complete Guide)
Step-by-step guide to monitoring Nano Banana Pro API quota in Google Cloud Console and AI Studio. Learn rate limits, quota checking methods, usage tracking, and practical solutions for quota management in December 2025.
Nano Banana Pro
4K-80%Google Gemini 3 Pro · AI Inpainting
谷歌原生模型 · AI智能修图
Running into 429 "quota exceeded" errors while using Nano Banana Pro API? Understanding where to check your quota and how to monitor usage effectively separates developers who hit walls from those who build reliable applications. The December 2025 quota adjustments have made this knowledge even more critical for anyone relying on Google's image generation capabilities.
This guide covers every method for checking your Nano Banana Pro API quota—from the Google Cloud Console dashboard to programmatic monitoring in your code. Whether you're using the free tier with its strict 50-100 daily limits or operating at enterprise scale with custom allocations, you'll learn exactly where to look and what to watch for.
Understanding Nano Banana Pro API Quota Structure
Before diving into the monitoring tools, understanding how Google structures API quotas prevents confusion when interpreting dashboard numbers. Nano Banana Pro operates under Google's Gemini API quota system, which tracks usage across four distinct dimensions.
Rate Limit Dimensions Explained:
| Dimension | Meaning | Typical Free Tier | Paid Tier 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| RPM | Requests per Minute | 5-10 | 300+ |
| TPM | Tokens per Minute | 250,000 | 1,000,000+ |
| RPD | Requests per Day | 50-100 | 1,000+ |
| IPM | Images per Minute | 5-10 | 100+ |
The system evaluates your usage against each limit independently. Exceeding any single dimension triggers a 429 error, even if other dimensions remain well within limits. For example, generating 11 images in one minute on the free tier violates IPM limits regardless of your daily quota status. For details on Gemini API rate limits, understanding these dimensions helps prevent unexpected 429 errors.
Important distinction: These limits apply per Google Cloud project, not per API key. Creating multiple API keys under the same project doesn't multiply your quota. However, creating separate projects does provide isolated quota pools—a strategy many developers use for production versus development environments.
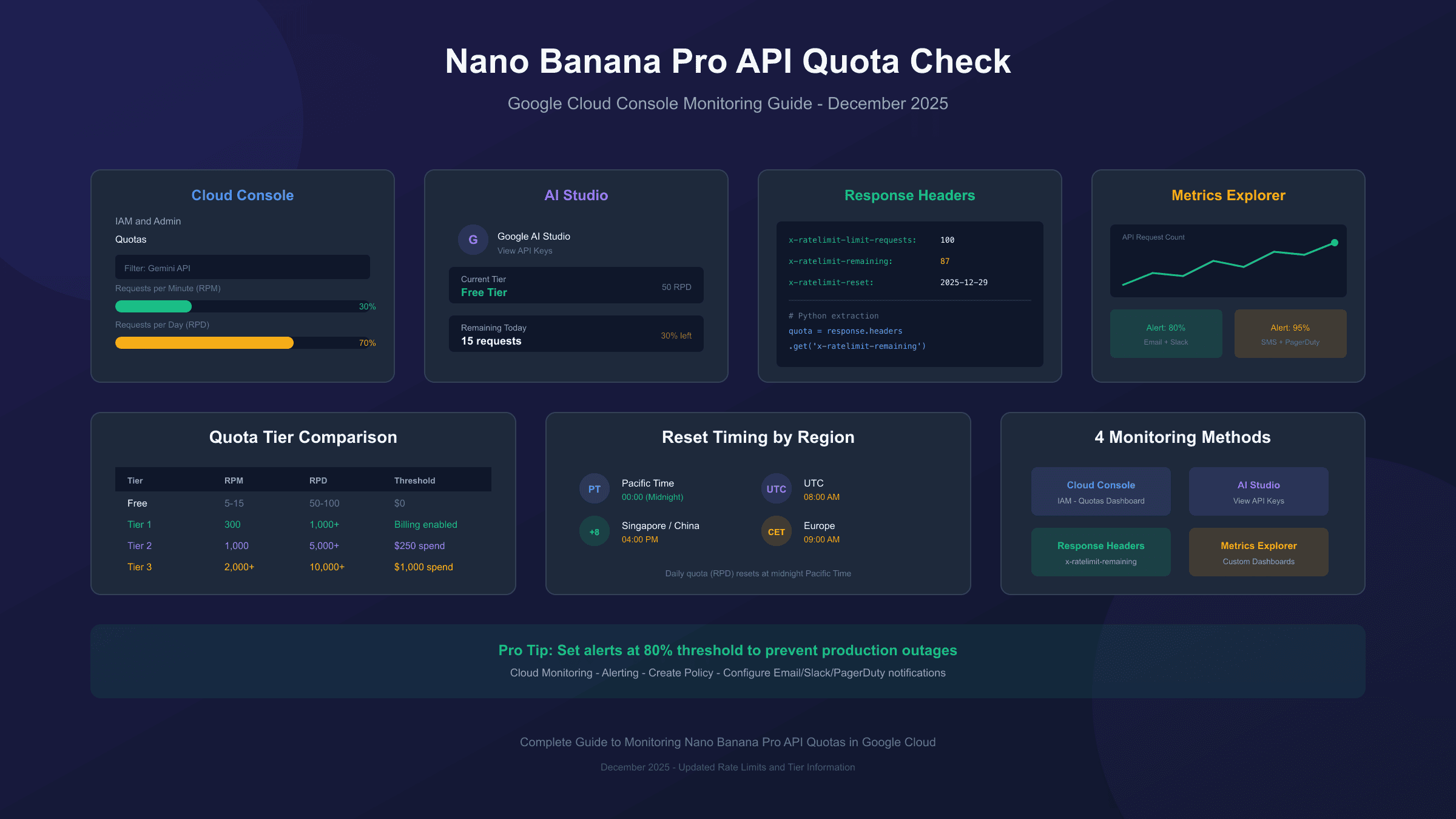
Method 1: Google Cloud Console Quota Dashboard
The most direct way to check Nano Banana Pro API quota is through Google Cloud Console's dedicated quota interface. This method provides real-time visibility into your current allocation and usage patterns.
Step-by-step access:
- Navigate to console.cloud.google.com
- Select your project from the dropdown menu
- Open the navigation menu (hamburger icon)
- Go to IAM & Admin → Quotas
- In the filter bar, search for "Gemini" or "Vertex AI"
The quota dashboard displays your allocated limits and current consumption. For Nano Banana Pro specifically, look for entries related to "Gemini API" or "Imagen" services. The dashboard updates approximately every few minutes, providing near-real-time visibility into usage patterns.
Key metrics to monitor:
- Current usage percentage: How much of your allocation you've consumed
- Peak usage: Maximum consumption during the viewing period
- Quota limit: Your allocated maximum for each dimension
- Reset timing: When daily quotas refresh (midnight Pacific Time)
Enterprise accounts may display custom quota allocations that differ from published documentation. If your numbers don't match public tier specifications, your organization likely has negotiated limits—check with your Google Cloud administrator for details.
Method 2: Google AI Studio Dashboard
For developers using the Gemini API directly (rather than through Vertex AI), Google AI Studio provides a more accessible quota monitoring interface. This method requires no Google Cloud Console access and works immediately after API key creation.
Accessing AI Studio quota information:
- Visit aistudio.google.com
- Sign in with your Google account
- Click on your profile icon in the upper right
- Select View API keys or navigate to the quota section
The AI Studio interface displays a simplified view of your current tier, remaining requests, and when limits reset. This method particularly suits individual developers and small teams who don't need the complexity of full Cloud Console access.
The December 2025 changes significantly impacted AI Studio users. Free tier limits dropped from approximately 250 requests per day to as few as 20 for some models. Monitoring through AI Studio helps you identify which specific models have the most restrictive limits in your current tier.
Method 3: API Response Header Monitoring
For programmatic quota tracking, the Gemini API includes rate limit information in response headers. This method enables real-time monitoring within your application code without requiring dashboard access.
Key headers to monitor:
hljs python# Example response headers (actual values vary by tier)
x-ratelimit-limit-requests: 100
x-ratelimit-limit-tokens: 250000
x-ratelimit-remaining-requests: 87
x-ratelimit-remaining-tokens: 243000
x-ratelimit-reset-requests: 2025-12-29T00:00:00Z
Python implementation for header extraction:
hljs pythonimport requests
def check_quota_from_response(response):
"""Extract quota information from API response headers."""
quota_info = {
'remaining_requests': response.headers.get('x-ratelimit-remaining-requests'),
'remaining_tokens': response.headers.get('x-ratelimit-remaining-tokens'),
'reset_time': response.headers.get('x-ratelimit-reset-requests'),
'limit_requests': response.headers.get('x-ratelimit-limit-requests')
}
return quota_info
# After any API call
response = requests.post(API_URL, headers=headers, json=payload)
quota = check_quota_from_response(response)
if int(quota['remaining_requests'] or 0) < 10:
print(f"Warning: Only {quota['remaining_requests']} requests remaining")
print(f"Quota resets at: {quota['reset_time']}")
This approach works for any API call—successful or failed. Failed requests (including 429 errors) still return header information, letting you determine exactly why the limit was hit and when it will reset.
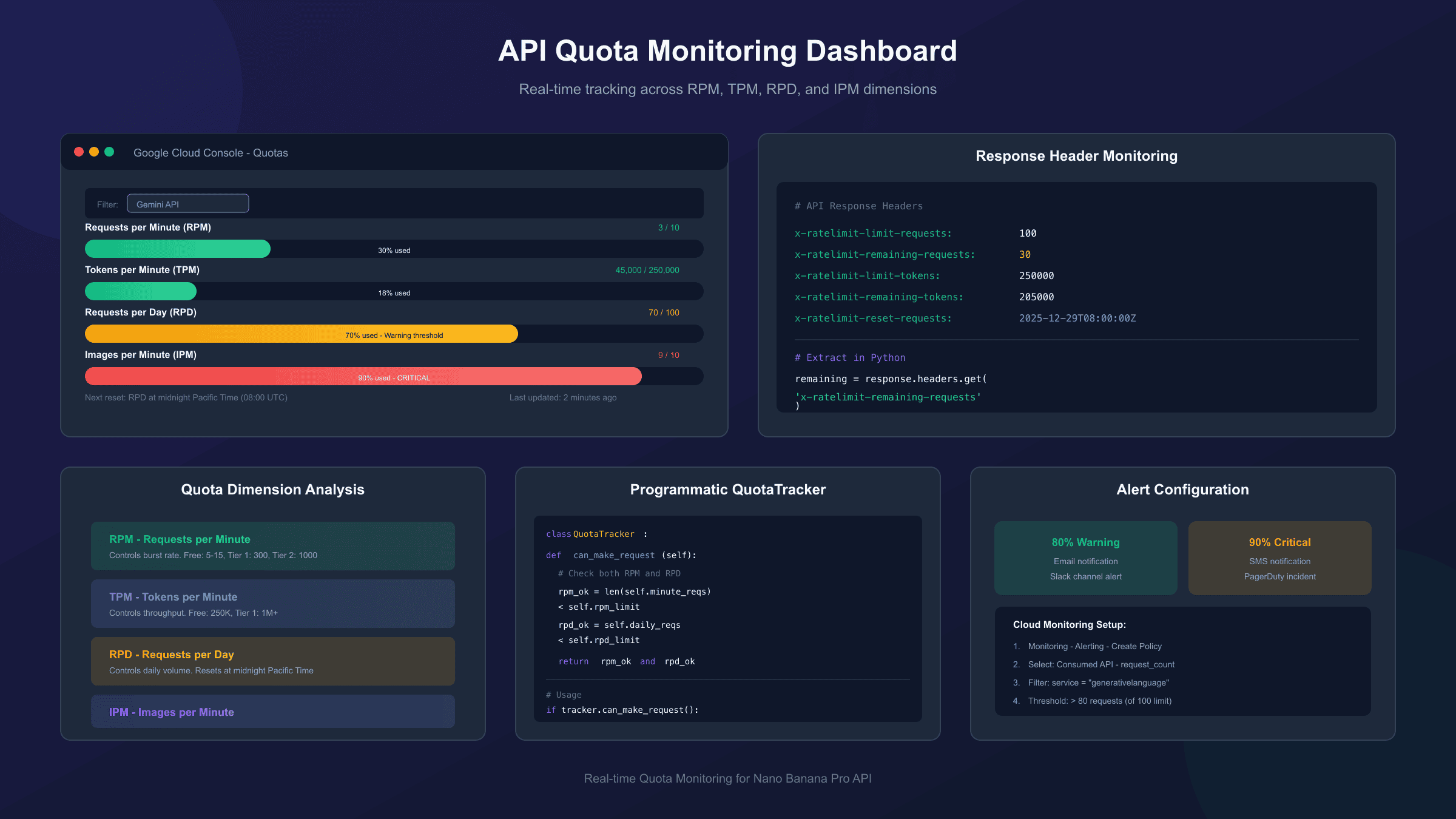
Method 4: Cloud Monitoring Metrics Explorer
For advanced monitoring with custom dashboards and alerts, Google Cloud Monitoring's Metrics Explorer provides the most powerful toolset. This method suits production applications requiring proactive notification when approaching quota limits.
Setting up quota monitoring:
- Navigate to Monitoring → Metrics Explorer in Cloud Console
- Select Consumed API as the resource type
- Choose relevant
serviceruntimemetrics - Apply filters for Gemini API or Vertex AI services
- Configure time ranges and aggregation methods
Creating quota alerts:
Cloud Monitoring supports automated alerts when metrics cross defined thresholds. Configure alerts at 80% quota consumption to receive notifications before hitting limits:
- Go to Monitoring → Alerting
- Create a new alerting policy
- Select your quota consumption metric
- Set threshold at 80% of your allocated limit
- Configure notification channels (email, SMS, Slack, PagerDuty)
This proactive approach prevents production outages by alerting teams before quota exhaustion occurs. The alert lead time allows for request throttling, quota increase requests, or failover to backup services.
Nano Banana Pro Free Tier Limits (December 2025)
The free tier underwent significant changes in December 2025. Understanding current limits helps set realistic expectations and plan usage accordingly.
Current free tier specifications:
| Model | RPM | TPM | RPD | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | 15 | 250,000 | 500 | Best free tier option |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | 5 | 250,000 | 100 | Reduced from previous levels |
| Imagen 3/4 | N/A | N/A | 10-20 | Very limited free access |
Critical limitation: Attempted requests count against quota even when they fail. A malformed request that returns a 400 error still consumes one request from your daily allocation. This behavior makes input validation before API calls essential for quota preservation.
Free tier limits reset at midnight Pacific Time (PT), not UTC. For developers in other time zones, this timing may not align with local business hours. Plan batch processing jobs to start shortly after the Pacific midnight reset to maximize available daily quota.
Paid Tier Quota Levels
Enabling billing on your Google Cloud project immediately upgrades quota allocation. The transition happens automatically—no manual tier change request required. For a complete breakdown of Nano Banana Pro pricing, understanding the cost structure helps plan budget allocation alongside quota planning.
Tier progression requirements:
| Tier | Spending Threshold | Typical RPM | Typical RPD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 5-15 | 50-100 |
| Tier 1 | $0+ (billing enabled) | 300 | 1,000+ |
| Tier 2 | $250 cumulative | 1,000 | 5,000+ |
| Tier 3 | $1,000 cumulative | 2,000+ | 10,000+ |
The $250 threshold for Tier 2 considers total Google Cloud spending, not just Gemini API usage. Organizations already using other Google Cloud services may qualify for higher tiers immediately after enabling Gemini API access.
Requesting quota increases:
For needs exceeding standard tier allocations:
- Navigate to IAM & Admin → Quotas in Cloud Console
- Find the specific quota you need increased
- Click the checkbox next to the quota
- Select Edit Quotas from the top menu
- Enter your requested limit and business justification
- Submit for review
Approval typically takes 24-72 hours for modest increases. Larger increases or new accounts may require additional review. Providing clear business justification—expected usage volume, growth projections, use case description—improves approval likelihood.
Quota Reset Timing and Time Zones
Understanding when quotas reset helps optimize usage patterns and avoid unnecessary errors near reset boundaries.
Reset schedule:
| Quota Type | Reset Time | Time Zone |
|---|---|---|
| RPM (per minute) | Every 60 seconds | N/A |
| RPD (per day) | Midnight | Pacific Time (PT) |
| Monthly billing | 1st of month | Pacific Time (PT) |
Midnight Pacific Time corresponds to different local times depending on your location:
- UTC: 8:00 AM (or 7:00 AM during PDT)
- GMT+8 (Singapore/China): 4:00 PM (or 3:00 PM during PDT)
- CET (Europe): 9:00 AM (or 8:00 AM during PDT)
For applications serving global users, consider implementing request queuing that holds non-urgent requests until after the reset window, maximizing the value of daily allocations.
Programmatic Quota Tracking Implementation
Building quota awareness directly into your application prevents unexpected failures and enables graceful degradation when approaching limits.
Complete quota tracking class:
hljs pythonimport time
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from collections import deque
class QuotaTracker:
"""Track API quota usage and predict exhaustion."""
def __init__(self, rpm_limit=10, rpd_limit=100):
self.rpm_limit = rpm_limit
self.rpd_limit = rpd_limit
self.minute_requests = deque()
self.daily_requests = 0
self.daily_reset = self._next_pacific_midnight()
def _next_pacific_midnight(self):
"""Calculate next midnight Pacific Time."""
# Simplified - production code should use pytz
now = datetime.utcnow()
pacific_offset = timedelta(hours=-8) # PST
pacific_now = now + pacific_offset
pacific_midnight = pacific_now.replace(
hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0
) + timedelta(days=1)
return pacific_midnight - pacific_offset
def can_make_request(self):
"""Check if a request can be made without hitting limits."""
self._cleanup_old_requests()
if datetime.utcnow() >= self.daily_reset:
self.daily_requests = 0
self.daily_reset = self._next_pacific_midnight()
rpm_ok = len(self.minute_requests) < self.rpm_limit
rpd_ok = self.daily_requests < self.rpd_limit
return rpm_ok and rpd_ok
def record_request(self):
"""Record a request was made."""
now = time.time()
self.minute_requests.append(now)
self.daily_requests += 1
def _cleanup_old_requests(self):
"""Remove requests older than 1 minute."""
cutoff = time.time() - 60
while self.minute_requests and self.minute_requests[0] < cutoff:
self.minute_requests.popleft()
def get_status(self):
"""Return current quota status."""
self._cleanup_old_requests()
return {
'rpm_used': len(self.minute_requests),
'rpm_remaining': self.rpm_limit - len(self.minute_requests),
'rpd_used': self.daily_requests,
'rpd_remaining': self.rpd_limit - self.daily_requests,
'next_reset': self.daily_reset.isoformat()
}
# Usage example
tracker = QuotaTracker(rpm_limit=10, rpd_limit=100)
if tracker.can_make_request():
# Make API call
response = generate_image(prompt)
tracker.record_request()
else:
status = tracker.get_status()
print(f"Rate limited. RPM remaining: {status['rpm_remaining']}")
print(f"Daily remaining: {status['rpd_remaining']}")
This implementation provides client-side tracking that complements server-side quota enforcement. It prevents unnecessary API calls when limits are already reached, saving both processing time and potentially improving your standing with Google's abuse detection systems.
Handling 429 Quota Exceeded Errors
When quota limits are hit despite monitoring efforts, proper error handling prevents application crashes and enables graceful recovery.
Recommended retry strategy:
hljs pythonimport time
import random
def generate_with_retry(prompt, max_retries=3):
"""Generate image with exponential backoff on quota errors."""
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
response = requests.post(API_URL, headers=headers, json={
"contents": [{"parts": [{"text": prompt}]}],
"generationConfig": {"responseModalities": ["IMAGE"]}
})
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.json()
if response.status_code == 429:
# Extract retry-after if available
retry_after = int(response.headers.get('Retry-After', 0))
if retry_after > 0:
wait_time = retry_after
else:
# Exponential backoff with jitter
wait_time = (2 ** attempt) + random.uniform(0, 1)
print(f"Rate limited. Waiting {wait_time:.1f}s before retry...")
time.sleep(wait_time)
continue
# Other errors - don't retry
response.raise_for_status()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
if attempt == max_retries - 1:
raise
time.sleep(2 ** attempt)
raise Exception("Max retries exceeded")
The Retry-After header, when present, provides the exact wait time recommended by Google's servers. Respecting this value demonstrates good API citizenship and may influence future quota increase requests.
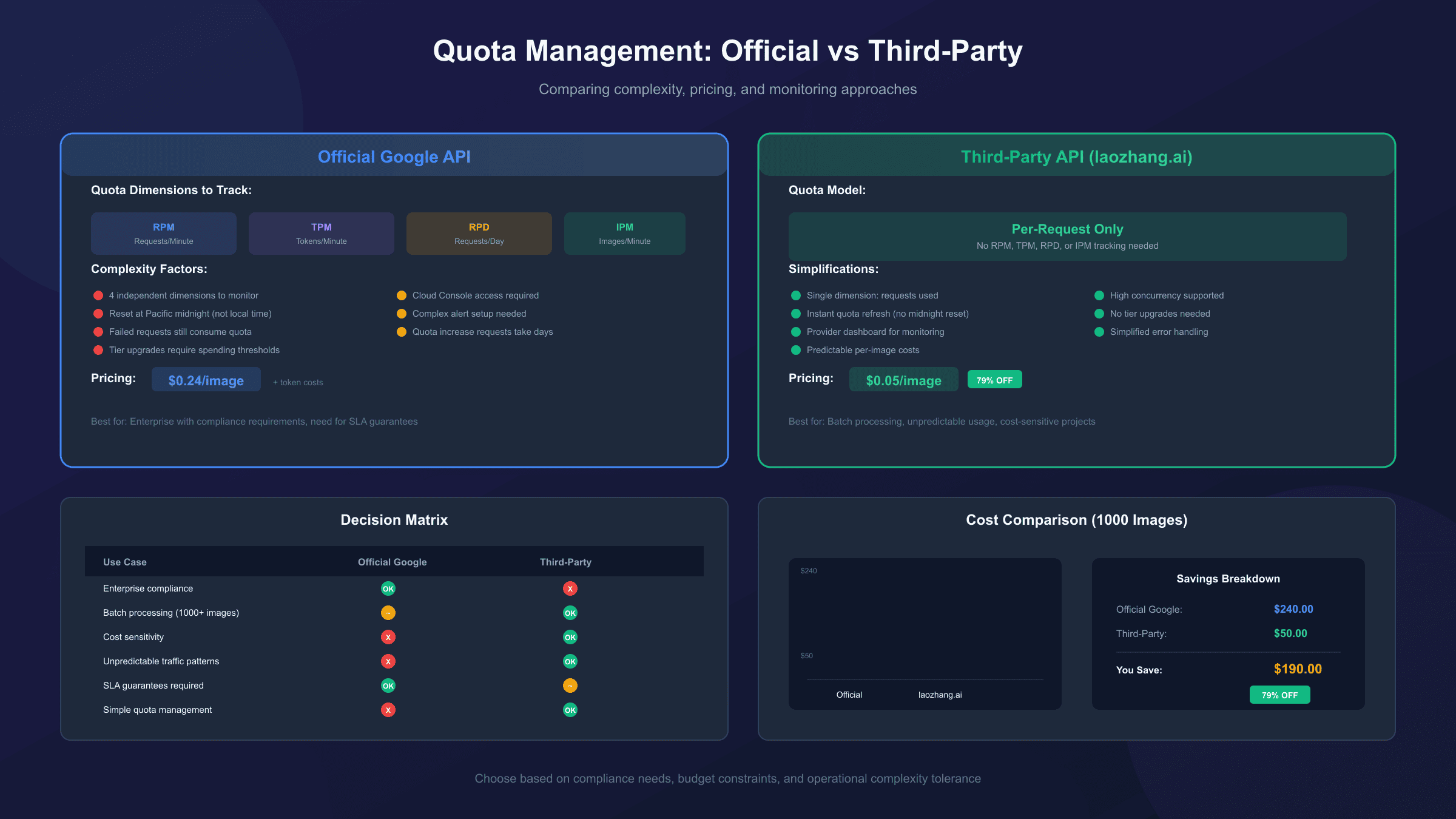
Alternative: Third-Party API Services
For developers who find Google's quota system restrictive or unpredictable, third-party API services offer an alternative approach with different quota characteristics. These services typically provide predictable per-request pricing without complex tier structures.
Third-party providers like laozhang.ai aggregate Nano Banana Pro access with simplified quota management. Instead of tracking RPM, TPM, RPD, and IPM separately, usage is billed per image generated at $0.05/image—a 79% reduction from Google's official pricing.
Comparison with official quota management:
| Aspect | Official Google API | Third-Party Services |
|---|---|---|
| Quota tracking | 4 dimensions (RPM/TPM/RPD/IPM) | Per-request only |
| Free tier | Limited, strict enforcement | Varies by provider |
| Pricing model | Token-based + request limits | Per-image flat rate |
| Reset complexity | Pacific midnight, 60s windows | Typically instant |
| Dashboard | Cloud Console required | Provider dashboard |
For batch processing or applications with unpredictable usage patterns, the simplified per-request model eliminates the need for complex quota tracking code. For those interested in comparing options, see our detailed API pricing comparison. However, official Google access provides direct support, guaranteed SLAs for enterprise accounts, and may be required for compliance-sensitive applications.
Setting Up Quota Alerts and Notifications
Proactive monitoring prevents production incidents better than reactive troubleshooting. Configure alerts before you need them.
Essential alert configurations:
-
80% Daily Quota Alert: Triggered when RPD consumption reaches 80%. Provides buffer time to reduce request rate or arrange alternative capacity.
-
Rate Limit Error Spike: Monitors 429 error count. Sudden increases indicate code changes, traffic spikes, or quota reductions.
-
Approaching Tier Threshold: For organizations near tier boundaries, alerts when spending approaches upgrade thresholds.
Cloud Monitoring alert configuration:
hljs yaml# Example alerting policy (conceptual - configure via Console)
alertPolicy:
displayName: "Gemini API Quota 80% Warning"
conditions:
- displayName: "Daily quota approaching limit"
conditionThreshold:
filter: 'resource.type="consumed_api" AND metric.type="serviceruntime.googleapis.com/api/request_count"'
comparison: COMPARISON_GT
thresholdValue: 80 # 80 requests of 100 limit
duration: 300s # 5 minute window
notificationChannels:
- projects/your-project/notificationChannels/email-channel
- projects/your-project/notificationChannels/slack-channel
Configure multiple notification channels for critical alerts. Email alone may not provide sufficient urgency for production issues; consider adding SMS or chat integration for high-priority alerts.
Best Practices for Quota Management
Effective quota management combines monitoring, code optimization, and architectural decisions.
Request optimization strategies:
-
Batch similar requests: Combine multiple prompts into single API calls where supported. This reduces RPM consumption while maintaining throughput.
-
Implement request queuing: During high-demand periods, queue non-urgent requests for processing after peak hours or reset windows.
-
Cache successful results: Store generated images rather than regenerating identical prompts. Many quota issues stem from accidentally duplicating requests.
-
Validate before calling: Check prompt validity, image dimensions, and other parameters before API calls. Failed validation still consumes quota.
Project organization:
- Separate development and production projects: Development testing shouldn't consume production quota.
- Use service accounts per application: Isolates quota tracking and simplifies debugging when limits are hit.
- Document quota dependencies: Ensure team members understand which applications depend on which quota pools.
Monitoring hygiene:
- Review quota dashboards weekly even when no issues occur
- Document baseline usage patterns for anomaly detection
- Test alert configurations periodically to ensure delivery
- Keep alert thresholds updated as usage patterns evolve
Troubleshooting Common Quota Issues
Issue: Quota shows available but requests still fail
Cause: RPM limit hit while RPD remains available. The dashboard may not refresh quickly enough to show minute-level consumption.
Solution: Implement client-side RPM tracking. Wait 60 seconds before retrying, or check response headers for exact remaining quota.
Issue: Quota usage higher than expected
Cause: Failed requests consuming quota, or multiple applications sharing project quota.
Solution: Audit all API keys under the project. Review error logs for failed requests. Consider separating applications into distinct projects.
Issue: Tier upgrade not reflected in quotas
Cause: Tier changes require billing history and may take up to 24 hours to propagate.
Solution: Verify billing is enabled and payment method is valid. Check billing history for required spending threshold. Contact Google Cloud support if delays exceed 48 hours.
Issue: Quota reset didn't occur at expected time
Cause: Time zone confusion—resets occur at Pacific Time, not local time or UTC.
Solution: Verify your local time conversion. During daylight saving transitions, reset times shift by one hour.
Conclusion
Monitoring Nano Banana Pro API quota effectively requires understanding Google's multi-dimensional quota system and implementing appropriate tracking at both dashboard and code levels. The December 2025 changes made this particularly important as free tier limits contracted significantly.
For production applications, combine Cloud Console monitoring with programmatic header tracking. Set up alerts at 80% thresholds to prevent unexpected outages. Consider quota requirements when architecting applications—the choice between official Google access and third-party services often depends more on quota management complexity than raw pricing.
Remember that quota limits exist to ensure fair access and service stability. Working within them—or properly requesting increases—maintains good standing with Google's systems and supports reliable long-term API access.
For developers finding quota management overhead excessive, third-party services offering per-image pricing eliminate the complexity of tracking four separate limit dimensions. Check our complete Nano Banana Pro guide for more implementation details. Evaluate whether the simplified model better fits your application's needs, especially for batch processing or unpredictable usage patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often do quota limits refresh? RPM (requests per minute) refreshes every 60 seconds. RPD (requests per day) resets at midnight Pacific Time. Monthly billing cycles reset on the 1st of each month Pacific Time.
Can I check quota without making an API call? Yes—use Google Cloud Console or AI Studio dashboards for real-time quota visibility. For programmatic access, the Cloud Monitoring API provides quota metrics without consuming Gemini API quota.
Do failed requests count against quota? Yes. Any request that reaches Google's servers consumes quota, regardless of whether it succeeds. Validate inputs before calling to avoid wasting quota on malformed requests.
How long does a quota increase request take? Modest increases typically approve within 24-72 hours. Larger increases or new accounts may require additional review. Providing clear business justification improves approval speed.
What's the difference between project quota and key quota? Quota applies per project, not per API key. Multiple keys under one project share the same quota pool. Create separate projects for isolated quota if needed.
Can I get notified before hitting quota limits? Yes. Configure Cloud Monitoring alerts at 80% thresholds to receive email, SMS, or chat notifications before limits are reached.